Motorola E680 Technical Manual - Page 94
Implementation based on Recommended Security, Policy, Trusted 3, Party Domain
 |
View all Motorola E680 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 94 highlights
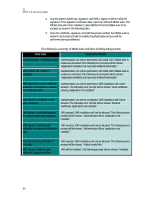
• oneshot - will prompt the user each time the protected API or function is requested by the MIDlet suite. (Always Ask) • No - will not allow the MIDlet suite access to the requested API or function that is protected. (No Access) The prompt No, Ask Later will be displayed during runtime dialogs and will enable the user to not allow the protected function to be accessed this instance, but to ask the user again the next time the protected function is called. User permission interaction modes will be determined by the security policy and device implementation. User permission will have a default interaction mode and a set of other available interaction modes. The user should be presented with a choice of available interaction modes, including the ability to deny access to the protected API or function. The user will make their decision based on the user-friendly description of the requested permissions provided for them. The Permissions menu allows the user to configure permission settings for each MIDlet when the VM is not running. This menu is synchronized with available run-time options. Implementation based on Recommended Security Policy The required trust model, the supported domain, and their corresponding structure will be contained in the default security policy for Motorola's implementation for MIDP 2.0. Permissions will be defined for MIDlets relating to their domain. User permission types, as well as user prompts and notifications, will also be defined. Trusted 3rd Party Domain A trusted third party protection domain root certificate is used to verify third party MIDlet suites. These root certificates will be mapped to a location on the handset that cannot be modified by the user. The following table shows the specific wording to be used in the first line of the above prompt: Protected Functionality Data network Data network (server mode) Comm Push SMS Top Line of Prompt "Send Data?" "Receive Data?" "Connect?" "Auto Start-Up?" "Use SMS?" 94