Omron HBF-516B Instruction Manual - Page 9
RESTING METABOLISM, 70% of daily energy use is for resting metabolism
 |
View all Omron HBF-516B manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 9 highlights
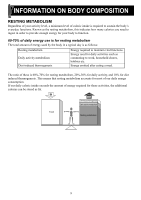
INFORMATION ON BODY COMPOSITION RESTING METABOLISM Regardless of your activity level, a minimum level of caloric intake is required to sustain the body's everyday functions. Known as the resting metabolism, this indicates how many calories you need to ingest in order to provide enough energy for your body to function. 60-70% of daily energy use is for resting metabolism The total amount of energy used by the body in a typical day is as follows: Resting metabolism Daily activity metabolism Diet-induced thermogenesis Energy required to maintain vital functions. Energy used for daily activities such as commuting to work, household chores, hobbies etc. Energy emitted after eating a meal. The ratio of these is 60%-70% for resting metabolism, 20%-30% for daily activity, and 10% for diet induced thermogenesis. This means that resting metabolism accounts for most of our daily energy consumption. If our daily caloric intake exceeds the amount of energy required for these activities, the additional calories can be stored as fat. Calories Calories Diet-induced thermogenesis Daily activity metabolism Food Resting metabolism 9