ProForm 695e English Manual - Page 15
Conditioning Guidelines
 |
View all ProForm 695e manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 15 highlights
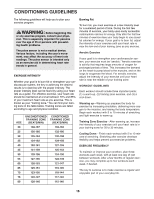
CONDITIONING GUIDELINES The following guidelines will help you to plan your exercise program. WARNING: Before beginning this or any exercise program, consult your physician. This is especially important for persons over the age of 35 or persons with pre-existing health problems. The pulse sensor is not a medical device. Various factors, including the userÕs movement, may affect the accuracy of heart rate readings. The pulse sensor is intended only as an exercise aid in determining heart rate trends in general. EXERCISE INTENSITY Whether your goal is to burn fat or strengthen your cardiovascular system, the key to achieving the desired results is to exercise with the proper intensity. The proper intensity level can be found by using your heart rate as a guide. For effective exercise, your heart rate should be maintained at a level between 70% and 85% of your maximum heart rate as you exercise. This is known as your Òtraining zone.Ó You can find your training zone in the table below. Training zones are listed according to age and physical condition. AGE 20 25 30 35 40 45 50 55 60 65 70 75 80 UNCONDITIONED TRAINING ZONE (BEATS/MIN) 138-167 136-166 135-164 134-162 132-161 131-159 129-156 127-155 126-153 125-151 123-150 122-147 120-146 CONDITIONED TRAINING ZONE (BEATS/MIN) 133-162 132-160 130-158 129-156 127-155 125-153 124-150 122-149 121-147 119-145 118-144 117-142 115-140 Burning Fat To burn fat, you must exercise at a low intensity level for a sustained period of time. During the first few minutes of exercise, your body uses easily accessible carbohydrate calories for energy. Only after the first few minutes of exercise does your body begin to use stored fat calories for energy. If your goal is to burn fat, adjust the intensity of your exercise until your heart rate is near the low end of your training zone as you exercise. Aerobic Exercise If your goal is to strengthen your cardiovascular system, your exercise must be Òaerobic.Ó Aerobic exercise is activity that requires large amounts of oxygen for prolonged periods of time. This increases the demand on the heart to pump blood to the muscles, and on the lungs to oxygenate the blood. For aerobic exercise, adjust the intensity of your exercise until your heart rate is near the middle of your training zone. WORKOUT GUIDELINES Each workout should include three important parts: (1) a warm-up, (2) training zone exercise, and (3) a cool-down. Warming upÑWarming up prepares the body for exercise by increasing circulation, delivering more oxygen to the muscles, and raising the body temperature. Begin each workout with 5 to 10 minutes of stretching and light exercise to warm up. Training Zone ExerciseÑAfter warming up, increase the intensity of your exercise until your heart rate is in your training zone for 20 to 30 minutes. Cooling DownÑFinish each workout with 5 to 10 minutes of stretching. Stretching after exercise develops flexibility and helps prevent post-exercise problems. EXERCISE FREQUENCY To maintain or improve your condition, plan three workouts each week, with at least one day of rest between workouts. After a few months of regular exercise, you may complete up to five workouts each week, if desired. The key to success is to make exercise a regular and enjoyable part of your everyday life. 15