Ricoh Aficio MP 7001 SP Design Guide - Page 18
to the @Remote Center GUI
 |
View all Ricoh Aficio MP 7001 SP manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 18 highlights
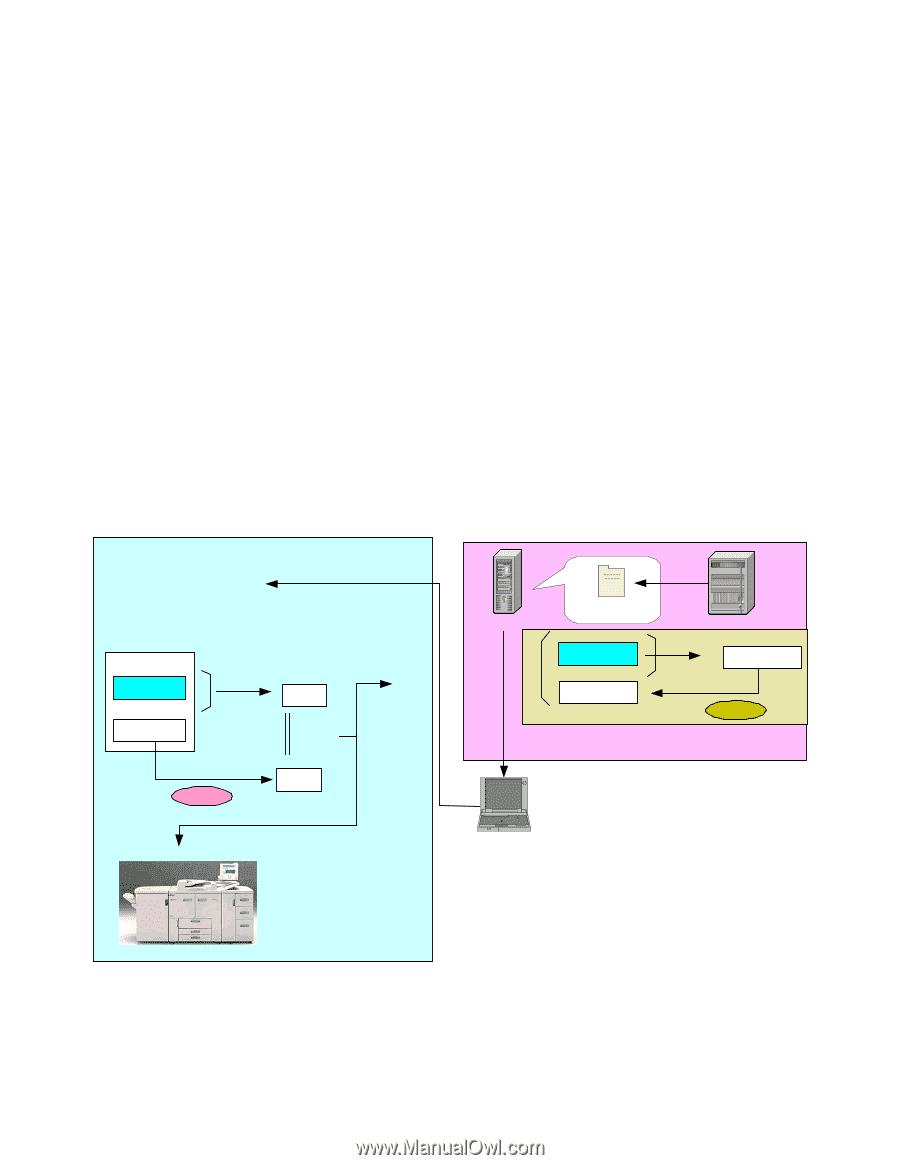
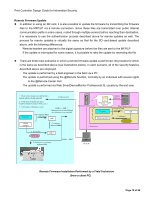
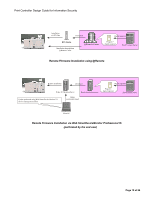
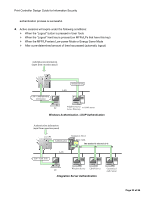
Print Controller Design Guide for Information Security Remote Firmware Update In addition to using an SD card, it is also possible to update the firmware by transmitting the firmware files to the MFP/LP via a remote connection. Since these files are transmitted over public Internet communication paths in some cases, routed through multiple servers before reaching their destination, it is necessary to use the authentication process described above for remote updates as well. The process for remote updates is virtually the same as that for the SD card-based update described above, with the following differences: Remote headers are attached to the digital signature before the files are sent to the MFP/LP. If the update is interrupted for some reason, it is possible to retry the update by resending the file. There are three main scenarios in which a remote firmware update is performed, the process for which is the same as described above (see illustrations below). In each scenario, all of the security features described above are employed. The update is performed by a field engineer in the field via a PC The update is performed using the @Remote function, normally by an individual with access rights to the @Remote Center GUI The update is performed via Web SmartDeviceMonitor Professional IS, usually by the end user 1. Check remote headers to confirm that a remote update is being requested 4. Files are sent 2. Verification of model and target machine functions (Copier, Printer, etc.) 3. Verification of firmware version Program 5. Generate MD1 using SHA-1 If MD1 ≠ MD2 Update process is cancelled and new firmware is not installed MD1 Digital signature 7. Compare MD and MD2 6. Decryption Public key MD2 8. Firmware is overwritten with new files If MD1 = MD2 Digital signature Ricoh distribution server Program + digital signature Program Ricoh license server 1. Generate MD using SHA-1 MD Digital signature 2. Generate digital signature Private key 3. Download Client PC Remote Firmware Installation Performed by a Field Technician (from a client PC) Page 18 of 86