Ryobi RYI2200 User Manual 5 - Page 12
Electrical - power refrigerator
 |
View all Ryobi RYI2200 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 12 highlights
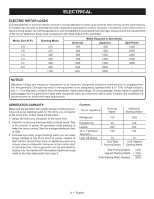
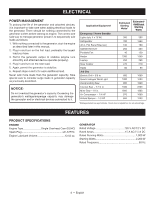
ELECTRICAL ELECTRIC MOTOR LOADS It is characteristic of common electric motors in normal operation to draw up to six times their running current while starting. This table may be used to estimate the watts required to start electric motors; however, if an electric motor fails to start or reach running speed, turn off the appliance or tool immediately to avoid equipment damage. Always check the requirements of the tool or appliance being used compared to the rated output of the generator. Motor Size (H.P.) 1/8 1/6 1/4 1/3 1/2 3/4 1 Running Watts 275 275 400 450 600 850 1100 Universal N/A 600 800 950 1000 1200 N/A Watts Required to Start Motor Capacitor Split Phase 850 1200 850 2050 1050 2400 1350 2700 1800 3600 2600 - 3300 - NOTICE: Operating voltage and frequency requirement of all electronic equipment should be checked prior to plugging them into this generator. Damage may result if the equipment is not designed to operate within a +/- 10% voltage variation, and +/- 3 hz frequency variation from the generator name plate ratings. To avoid damage, always have an additional load plugged into the generator if solid state equipment (such as a television set) is used. A power line conditioner is recommended for some solid state applications. GENERATOR CAPACITY Make sure the generator can supply enough continuous (running) and surge (starting) watts for the items you will power at the same time. Follow these simple steps. 1. Select the items you will power at the same time. 2. Total the continuous (running) watts of these items. This is the amount of power the generator must produce to keep the items running. See the wattage reference chart at right. 3. Estimate how many surge (starting) watts you will need. Surge wattage is the short burst of power needed to start electric motor-driven tools or appliances such as a circular saw or refrigerator. Because not all motors start at the same time, total surge watts can be estimated by adding only the item(s) with the highest additional surge watts to the total rated watts from step 2. Example: Tool or Appliance Running Watts* Additional Starting Watts* Refrigerator 700 1350 Portable Fan Laptop 46 in. Flat Panel Television Light (75 Watts) 40 250 190 75 1255 Total Running Watts 120 250 190 75 1350 Highest Starting Watts Total Running Watts Highest Starting Watts Total Starting Watts Needed 1255 + 1350 2605 8 - English