SanDisk SDSDB-016G-A11 Product Manual - Page 10
SD Status, Block, Sector, WP Group
 |
UPC - 619659055639
View all SanDisk SDSDB-016G-A11 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 10 highlights
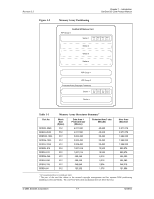
Revision 2.2 Chapter 1 - Introduction SanDisk SD Card Product Manual • SD Status is stored in 512 bits that are sent as a single data block after it was requested by the host using the SD_STATUS (ACMD13) command. SD_STATUS contains extended status bits that relate to BUS_WIDTH, security related bits and future specific applications. 1.12.5 Memory Array Partitioning The basic unit of data transfer to/from the SanDisk SD Card is one byte. All data transfer operations that require a block size always define block lengths as integer multiples of bytes. Some special functions need other partition granularity. Figure 1-2 shows the Memory Array Partitioning. For block-oriented commands, the following definition is used: • Block-A unit related to block-oriented read and write commands. Its size is the number of bytes that are transferred when one block command is sent by the host. The size of a block is either programmable or fixed; information about allowed block sizes and the programmability is stored in the CSD Register. The granularity of the erasable units is, in general, not the same as for the block-oriented commands: • Sector-A unit related to the erase commands. Its size is the number of blocks that are erased in one portion. The size of a sector is fixed for each device. The information about the sector size (in blocks) is stored in the CSD Register. For devices that include write protection, the following definition is used: • WP Group-A minimal unit that may have individual write protection. Its size is the number of groups to be write protected by one bit. The size of a WP group is fixed for each device. The information about the size is stored in the CSD Register. © 2004 SanDisk Corporation 1-6 12/08/04