ASRock Q77M vPro Quick Start Guide - Page 7
Step 1, Con Existing IT Infrastructure - processor
 |
View all ASRock Q77M vPro manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 7 highlights
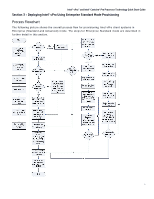
Intel® vPro™ and Intel® Centrino® Pro Processor Technology Quick Start Guide Step 1: Configure Existing IT Infrastructure In order for an Intel vPro machine to be manageable, it must become known to the management console. The process by which this occurs is called "provisioning". Enterprise setup (pre-provisioning) requires a series of steps that are performed on both the Intel vPro clients and the SCS in order to prepare the client for provisioning over the network by the SCS (which acts as the provisioning server for the Intel vPro clients). Intel vPro Integration Points with IT Infrastructure Components The following diagram shows the interaction with the different network elements. Each will be discussed briefly in order to understand the integration requirement. Intel® vPro™ Clients Manages Manages Core Server Configuration Server CA Server Management Console Registers Requests Updates SQL DB DHCP DNS DHCP Server: When an Intel vPro machine enters setup state, the default IP addressing scheme is DHCP (that is, use DHCP to obtain an IP address). The Intel® Management Engine (Intel® ME) also uses the DHCP server to help dynamically update the DNS server with its network address information. The DHCP server must support Option 81 to register network address information into the DNS server on behalf of the Intel ME. Option 15 should also be enabled in the DHCP Scope Options to allow the DNS to resolve host queries after IP address changes. DNS Server: The DNS Server is used by network devices such as Management Consoles to locate address information for Intel vPro clients in order to contact them and manage them. The Intel vPro clients may also use the DNS server during the provisioning configuration phase to locate the provision server and request their configuration information, as explained below. Once configured to the setup state, Intel AMT makes a DNS request for the name "ProvisionServer" (unless you choose to configure the client's BIOS manually). If the requested name cannot be resolved by the DNS server, then a second request is made for "ProvisionServer.DomainName." Intel AMT expects to either find the IP address of the provision server in this way, or by having it set explicitly in the Intel MEBX configuration process (Step 4: Configure Intel vPro Client Authentication Settings, page 10). The Intel Management Engine BIOS Extension (Intel MEBX) is an option ROM module extension to the system BIOS, provided to the OEM by Intel. The Intel MEBX allows you to configure settings that 7