ATI X1800 User Guide - Page 120
ATI Catalyst™ Control Center interface., Super Anti-aliasing modes operate in this manner
 |
UPC - 727419412575
View all ATI X1800 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 120 highlights
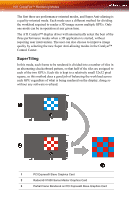
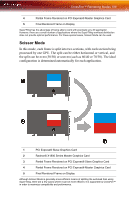
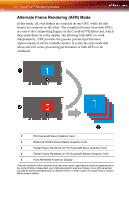
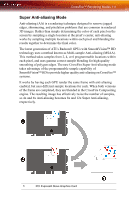
112 CrossFire™ Rendering Modes 2 Radeon® X1800 Series Master Graphics Card 3 Partial Frame Rendered on PCI Express® Slave Graphics Card 4 Partial Frame Rendered on PCI Express® Master Graphics Card 5 Final Rendered Frame on Display Some types of textures, especially those with transparent portions, can exhibit aliasing that is not removed by MSAA techniques. Another form of anti-aliasing, known as Super-sample Anti-aliasing (SSAA), can be useful in these cases, because it affects every pixel in an image. Although it normally operates more slowly than MSAA, the power of multiple GPUs can make SSAA practical to use. SSAA first renders a scene at a higher resolution than that which is output to the display, which is then downsampled to the display's resolution. This approach normally has two main disadvantages: it requires rendering many more pixels than normal, which can have a drastic impact on performance, and that it results in an ordered grid sample pattern, which does a poor job of anti-aliasing some types of jagged edges. CrossFire™'s Super Antialiasing overcomes both of these problems. It takes advantage of the second GPU to render the additional pixels required for each frame, so there is little or no performance impact. It can also make use of a more effective sample pattern that does a better job of anti-aliasing near-horizontal and nearvertical edges, resulting in better overall image quality. Two of the new Super Anti-aliasing modes use a combination of MSAA and SSAA to achieve the ultimate in image quality. They work by not only using different multi-sample locations on each GPU, but also by offsetting the pixel centers slightly. In effect, each GPU renders the image from a different viewpoint, about half a pixel width apart. The new 10x and 14x Super Anti-aliasing modes operate in this manner, combining 2x SSAA with 4x and 6x MSAA, respectively. Both of these modes work together with SmoothVision™ HD Anisotropic Filtering (AF). This filtering technique produces sharper, clearer textures by blending multiple texture samples (2, 4, 8, or 16) for each pixel. Because Super Anti-aliasing can render each pixel from two slightly different viewpoints and combine them, the texture samples from each viewpoint are combined as well. This means the number of texture samples per pixel is effectively doubled, so up to 32x Anisotropic Filtering can be supported. The new Super Anti-aliasing modes can be enabled by users through the ATI Catalyst™ Control Center interface.