Cisco 7931G Administration Guide - Page 62
Unified Communications Manager on the list. If, Unified IP Phone communicates with Cisco - phone manual
 |
UPC - 882658128578
View all Cisco 7931G manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 62 highlights
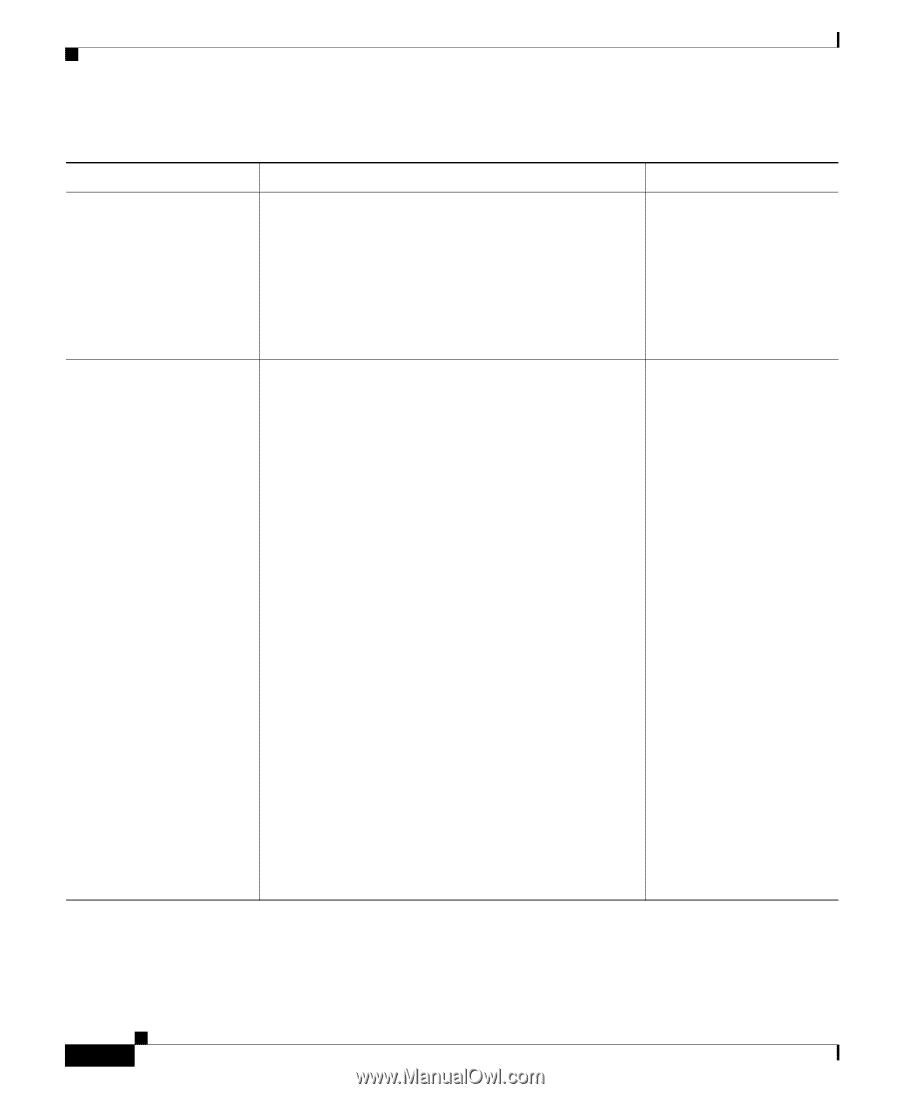
Understanding the Phone Startup Process Chapter 2 Preparing to Install the Cisco Unified IP Phone on Your Network Table 2-3 Cisco Unified IP Phone Startup Process (continued) Process Step 7. Requesting the Configuration File 8. Contacting Cisco Unified Communications Manager Description Related Topics The TFTP server has configuration files, which define parameters for connecting to Cisco Unified Communications Manager and other information for the phone. See the "Understanding Phone Configuration Files" section on page 2-6. See the "Resolving Startup Problems" section on page 9-2. The configuration file defines how the Cisco Unified IP Phone communicates with Cisco Unified Communications Manager and provides a phone with its load ID. After obtaining the file from the TFTP server, the phone attempts to make a connection to the highest priority Cisco Unified Communications Manager on the list. If security is implemented, the phone makes a TLS connection. Otherwise, it makes a non-secure TCP connection. See the "Resolving Startup Problems" section on page 9-2. If the phone was manually added to the database, Cisco Unified Communications Manager identifies the phone. If the phone was not manually added to the database and auto-registration is enabled in Cisco Unified Communications Manager, the phone attempts to auto-register itself in the Cisco Unified Communications Manager database. Note Auto-registration is disabled when security is enabled on Cisco Unified Communications Manager. In this case, the phone must be manually added to the Cisco Unified Communications Manager database. 2-10 Cisco Unified IP Phone 7931G Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager 6.0 OL-12457-01