Dell PowerVault 51F Dell PowerVault 51F 8-Port Fibre Channel Switch Insta - Page 50
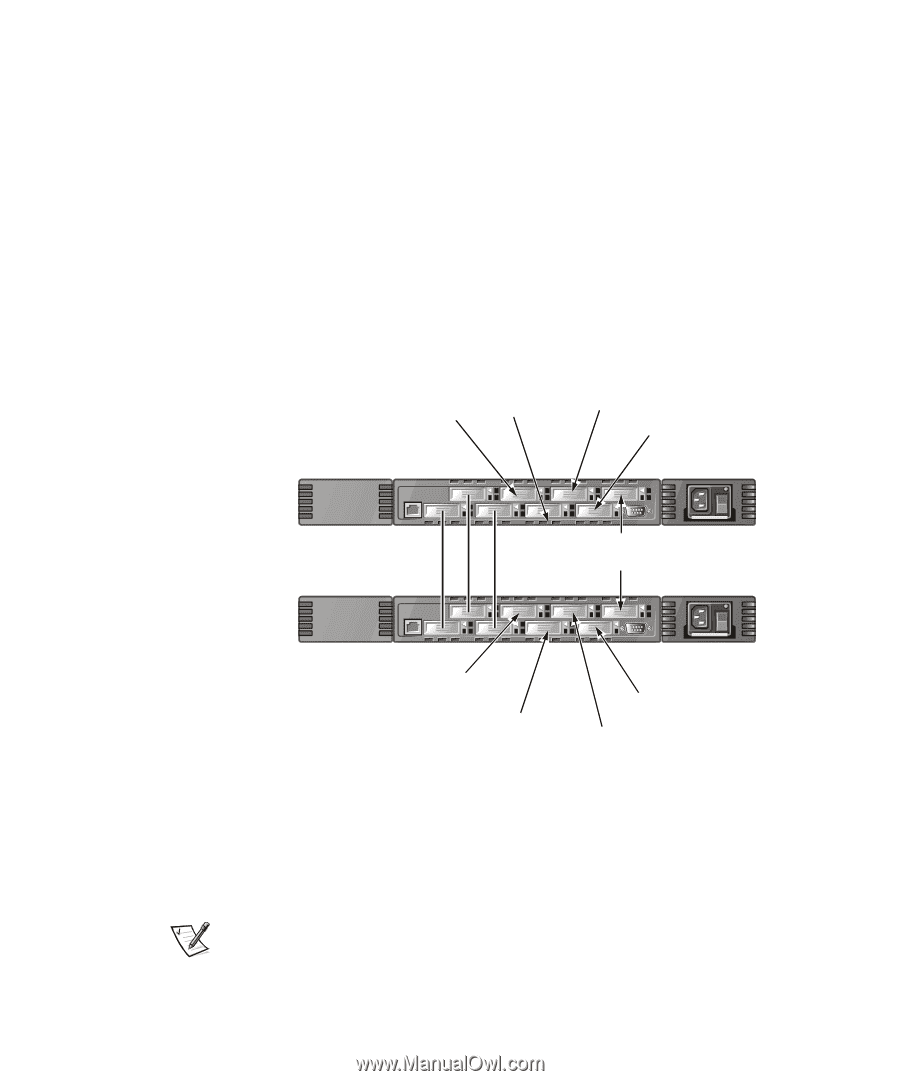
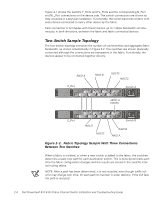
Two-Switch Sample Topology, Fabric Topology Sample With Three Connections
 |
View all Dell PowerVault 51F manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 50 highlights
FILE LOCATION: S:\SYSTEMS\Boxer\rev_i&t\English\50UWDa00\50UWDc20.fm Figure 2-1 shows the switch's F_Ports and FL_Ports and the corresponding N_Port and NL_Port connections on the device side. The switch connections are shown as they would be in a physical installation. Functionally, the switch becomes a fabric with every device connected to every other device by the fabric. Each connection is full duplex with transmissions up to 1 Gbps bandwidth simultaneously, in both directions, between the fabric and fabric-connected devices. Two-Switch Sample Topology The two-switch topology increases the number of connectivities and aggregate fabric bandwidth, as shown schematically in Figure 2-2. The switches are shown physically connected although the connections are transparent in the fabric. Functionally, the devices appear to be connected together directly. RAID A E_Port RAID B HOST3 HOST4 Switch A JBOD A HOST5 E_Port HOST1 HOST2 Switch B RAID B RAID A Figure 2-2. Fabric Topology Sample With Three Connections Between Two Switches When a fabric is initiated, or when a new switch is added to the fabric, the switches determine a least-cost path for each destination switch. This is done dynamically each time the fabric configuration changes and the results are stored in the switch's internal routing tables. NOTE: After a path has been determined, it is not rerouted, even though traffic volume may change over time, for each path to maintain in-order delivery. If the link fails, the path is rerouted. DELL CONFIDENTIAL - Preliminary 4/6/00 2-4 Dell PowerVault 51F 8-Port Fibre Channel Switch Installation and Troubleshooting Guide