Dell PowerVault MD3200 Deployment Guide - Page 10
About the Storage Array Connections, Cabling the Storage Array - sas storage
 |
View all Dell PowerVault MD3200 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 10 highlights
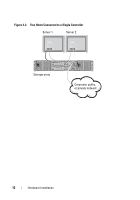
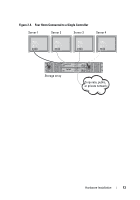
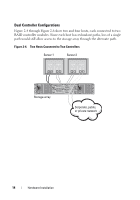
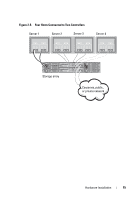
About the Storage Array Connections The storage array is connected to a host using two hot-swappable RAID controller modules. The RAID controller modules are identified as RAID controller module 0 and RAID controller module 1. For more information, see the Getting Started Guide. Each RAID controller module has four SAS In port connectors that provide SAS connections to the host or node. Each RAID controller module also contains an Ethernet management port and a SAS Out port connector. The Ethernet management port allows you to install a dedicated management station (server or stand-alone system). The SAS Out port allows you to connect the storage array to optional expansion enclosures for additional storage capacity. For more information, see the Getting Started Guide. Each PowerVault MD3200 Series storage array can be expanded to a maximum of 96 physical disks through a maximum of seven PowerVault MD1200 Series expansion enclosures. NOTE: When you connect a host server to a storage array SAS In port connector, any Out port connector of the server's host bus adapter (HBA) can be used. Cabling the Storage Array You can cable the storage array to host servers with: • Single path data configuration-A single path configuration allows you to connect a maximum of eight hosts. This is a non-redundant configuration. • Dual path data configuration-A dual path configuration allows you to connect a maximum of four hosts. You choose the data configuration based on: • Number of hosts required • Level of data redundancy required Redundant and Non-Redundant Configurations Non-redundant configurations are configurations that provide only a single data path from a host to the storage array. This type of configuration is only recommended for non-critical data storage. Path failure from a failed or removed cable, a failed HBA, or a failed or removed RAID controller module results in loss of host access to storage on the storage array. 10 Hardware Installation