Dell Precision R5400 Remote Access Device: Networking Considerations - Page 7
Segment the User Base
 |
View all Dell Precision R5400 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 7 highlights
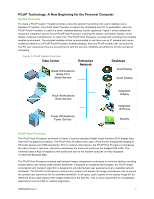
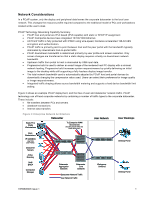
Network Capacity - is the capacity of the network to forward packets, described in bits per second. Networks may have any number of capacity constrictions, including link-rates between switches, or internal switching limits of the switches themselves. This term is used in this document to describe the ability of the network to forward network data relative to the link planning bandwidth. Device Bandwidth Limit - is a configuration parameter in PCoIP hosts and portals that is a hard upper bandwidth limit between the PCoIP hosts and portal pairs for downstream (host to portal) and upstream (portal to host) traffic. This feature is available for advanced IT configurations, and it is recommended that the default setting (disabled) be used in most environments. Disabling the Device Bandwidth Limit allows the PCoIP host and portal pair to make optimal use of the available network resources. While the Device Bandwidth Limit is normally disabled, an IT administrator may use the setting to get a feel for the relationship between used network bandwidth and user experience. Through experimentation with content typically seen by the user, the IT person may find that the network bandwidths described in this document are too conservative and adjust the values accordingly. Device Bandwidth Target - is a configuration parameter in the PCoIP host and portal that defines the bandwidth that each attempts to maintain when the network is congested. This setting allows IT administrators to set a soft bandwidth floor for all users to improve the fair distribution of bandwidth when the network is congested. When the network is not undergoing congestion, the PCoIP devices will adapt to use available bandwidth as required, up to the Device Bandwidth Limit. The Device Bandwidth Target should be set to the Planning Bandwidth to ensure that each user maintains a minimal acceptable experience level in a constrained network scenario. Peak Bandwidth - is the maximum bandwidth for a given user PCoIP host and portal pair. Since PCoIP only transmits changes in the user's display, large screen change results in a burst of network traffic. The peak is defined by the display resolution and the number of pixels changing at a given time. The Device Bandwidth Limit may be set to impose a limit on the peak bandwidth. Average Bandwidth - is the average bandwidth for a given user PCoIP host and portal pair over a long period of time. The average bandwidth is very application and user dependent but is typically a small fraction of the peak bandwidth. Segment the User Base PCoIP network requirements are highly dependant on the usage scenario, ranging from plain text data entry to 3D CAD. To understand the optimal network size and networking settings, IT administrators need to use their understanding of the user base. Table 1 shows common user types and associated profiles. Table 1: Example User Segmentation to Optimize Network Resource Allocation User Category User Profile Task Worker Knowledge Worker/ Basic CAD Performance User/ 3D Modeling Video Editing Extreme User Primarily text entry into forms. Uses standard office applications such as word processing, spreadsheets, and presentation tools, uses web, reads and writes emails, and simple CAD applications etc. Similar to the Knowledge Worker user profile with the exception of occasional use of high-end visual applications, 3D modeling and may perform analysis on static images. Similar to performance user, but requires consistent high-quality multimedia playback. Discerning users of high-end visual applications such as 3D modeling, video editing or animation. Typically content has a higher resolution and the user performs technical analysis by dynamically manipulating images. TER0806005 Issue 1 7