HP 2000sa RAID 6 with HP Advanced Data Guarding technology: a cost-effective, - Page 2
Abstract, Introduction
 |
View all HP 2000sa manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 2 highlights
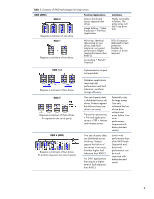
Abstract RAID 6 with HP's patented Advanced Data Guarding (ADG) technology is a cost-effective solution for storing large volumes of enterprise data with fault tolerance. Its performance, like that of other RAID levels, depends on the nature of the application. Organizations implementing a large drive array should consider RAID 6 because it can tolerate up to two simultaneous drive failures without downtime or data loss. By differentiating among the available RAID schemes, this paper provides information to help IT managers select the RAID scheme that will best meet all the needs of their specific computing environment. Introduction An increasingly important IT challenge is finding cost-effective storage technologies to protect the data that businesses amass as a result of e-business and traditional applications such as transaction processing, enterprise resource planning, and decision analysis. An effective storage solution must meet three very important needs: fault tolerance, efficient use of storage capacity, and high performance. Organizations implementing a large storage array should consider an HP RAID 6 solution because it can tolerate up to two simultaneous drive failures without downtime or data loss. This paper describes the functions and limitations of available RAID schemes for protecting data in large storage systems. It describes the most important factors for consideration in choosing a storage solution. By differentiating among the available RAID1 schemes, this paper provides information to help IT managers select the RAID scheme that will best meet all the needs of their specific computing environment. 1 RAID is an acronym for redundant array of independent disks. 2