HP ML530 RDMA protocol: improving network performance - Page 4
RDMA over TCP, Sending Host
 |
UPC - 720591250669
View all HP ML530 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 4 highlights
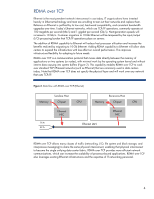
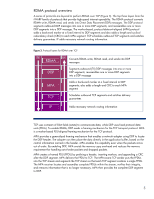
RDMA over TCP Ethernet is the most prevalent network interconnect in use today. IT organizations have invested heavily in Ethernet technology and most are unwilling to tear out their networks and replace them. Reliance on Ethernet is justified by its low cost, backward compatibility, and consistent bandwidth upgrades over time. Today's Ethernet networks, which use TCP/IP operations, commonly operate at 100 megabits per second (Mb/s) and 1 gigabit per second (Gb/s). Next-generation speeds will increase to 10 Gb/s. Customer migration to 10-Gb Ethernet will be tempered by the input/output (I/O) processing burden that TCP/IP operations place on servers. The addition of RDMA capability to Ethernet will reduce host processor utilization and increase the benefits realized by migrating to 10-Gb Ethernet. Adding RDMA capability to Ethernet will allow data centers to expand the infrastructure with less effect on overall performance. This improves infrastructure flexibility for adapting to future needs. RDMA over TCP is a communication protocol that moves data directly between the memory of applications on two systems (or nodes), with minimal work by the operating system kernel and without interim data copying into system buffers (Figure 2). This capability enables RDMA over TCP to work over standard TCP/IP-based networks (such as Ethernet) that are commonly used in data centers today. Note that RDMA over TCP does not specify the physical layer and will work over any network that uses TCP/IP. Figure 2. Data flow with RDMA over TCP (Ethernet) Memory Sending Host Chipset TX Pr RX Pr Ethernet NIC Receiving Host CPU Memory Chipset CPU Ethernet NIC Ethernet LAN RDMA over TCP allows many classes of traffic (networking, I/O, file system and block storage, and interprocess messaging) to share the same physical interconnect, enabling that physical interconnect to become the single unifying data center fabric. RDMA over TCP provides more efficient network communications, which can increase the scalability of processor-bound applications. RDMA over TCP also leverages existing Ethernet infrastructures and the expertise of IT networking personnel. 4