LG GR-K18PBS Service Manual - Page 51
Caution
 |
View all LG GR-K18PBS manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 51 highlights
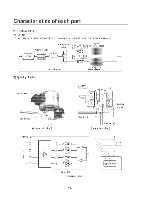
Characteristics of each part 9-1-7. Capacitor operating principle and temperature characteristics (1) Function 1. Capacitor (CIS): Sometimes called the starting capacitor, it is used to improve the motor operation characteristics in low pressure because the operating torque is weak based on the characteristics of the motor within the compressor of the refrigerator in low voltage areas (85% or less than rated). 2. Capacitor (C/R): Sometimes called the running capacitor, it is used to improve the operating torque of the motor within the compressor of the refrigerator. (Capacitor for operation) (2) Concept When you put dielectric material between two facing electrodes and connect the voltage, the electric charge will be accumulated. This functional device is called a capacitor and the basic structure is as shown in the right figure. (3) Poor symptom (product) A electrode - - 17 Dielectric material B electrode Problem (parts) Symptom ❑isconnected (open) Shorted Normal 1) Compressor does not work. 2) Compressor is heated. 3) OLP is operating. 4) Power fuse is disconnected. (Immediately after exchanging or frequently) Check method - Measure the both ends of the capacitor with a tester to see if there is no change: O. LI. Resolution - Exchange the capacitor 1) Compressor does not work. 2) Compressor is heated. 3) Compressor repeatedly works and stops. 4) OLP is operating. 5) Power fuse is disconnected. (Immediately after exchanging or frequently) - Measure the both ends of the capacitor with a tester to see if it is 0 c≥. - Exchange the capacitor 1) Compressor does not work. 2) Compressor is heated. 3) Compressor repeatedly works and stops. 4) OLP is operating. 5) Power fuse is disconnected. (Immediately after exchanging or frequently) - Measure the both ends of the capacitor with a tester to see if it decreases and then slowly increases (Move toward 0 a and then to - LI). - Check other parts Caution ► Before the measurement, short the capacitor with a driver to discharge all the electricity. ► After setting the multiplier rate to maximum within the resistance measuring range, measure while switching the terminals. - 51 -