Lexmark E360DN Technical Reference - Page 18
Electrical specifications, Power requirements, E260, E260d/dn, E360d/E360dn, and E460dn/E460dw - fuser
 |
UPC - 734646084475
View all Lexmark E360DN manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 18 highlights
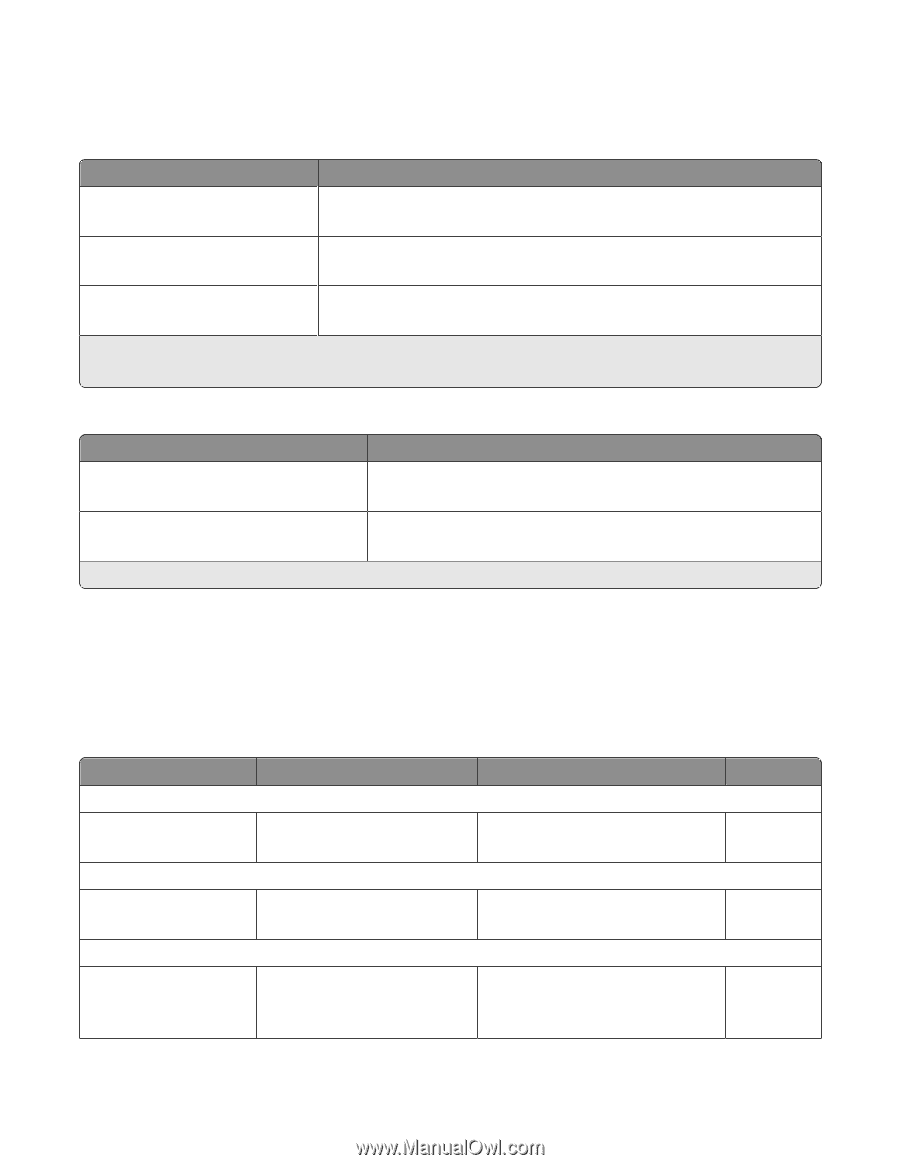
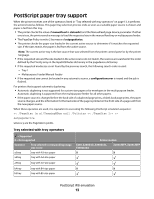
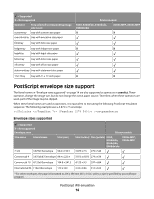
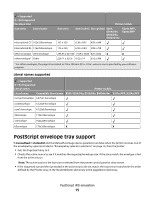
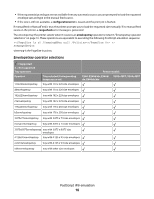
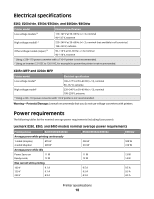
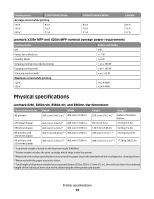
Electrical specifications E260, E260d/dn, E360d/E360dn, and E460dn/E460dw Printer model Electrical specification Low voltage models1,2 110-127 V at 50-60 Hz (+/- 3), nominal 90-137 V, extreme High voltage models1,2 220-240 V at 50-60 Hz (+/- 3), nominal (not available in all countries) 198-259 V, extreme Other voltage models (Japan)1,2 90-110 V at 50-60 Hz (+/-3), nominal 90-110 V, extreme 1 Using a 220-110 power converter with a 110-V printer is not recommended. 2 Using an inverter (12 V DC to 120 V AC, for example) to power the printer is not recommended. X203n MFP and X204n MFP Printer model Electrical specification Low voltage model* 100-127 V at 50-60 Hz (+/-3), nominal 90-137 V, extreme High voltage model* 220-240 V at 50-60 Hz (+/-3), nominal 198-259 V, extreme * Using a 220-110 power converter with 110 V printer is not recommended. Warning-Potential Damage: Lexmark recommends that you do not use voltage converters with printers. Power requirements The following tables list the nominal average power requirements (including fuser power). Lexmark E260, E360, and E460 models nominal average power requirements Printing states E260/E260d/E260dn Average power while printing continuously 1-sided (simplex) 2-sided (duplex) 470 W 290 W Average power while idle Power Saver on Ready mode 11 W 12 W Max current while printing 100 V 120 V 230 V 9.1 A 9.1 A 4.5 A E360d/E360dn/E460dn 500 W 310 W 11 W 12 W 9.5 A 9.5 A 4.5 A E460dw 500 W 310 W 13 W 14 W 9.5 A 9.5 A 4.5 A Printer specifications 18