Netgear DGND3700v1 [English]: DGND3700 User Manual (PDF) - Page 139
Static Routes, Static Route Example
 |
View all Netgear DGND3700v1 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 139 highlights
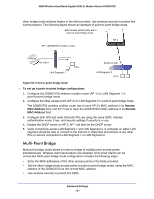
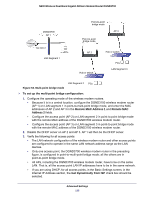
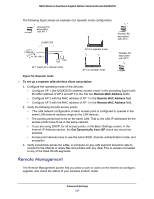
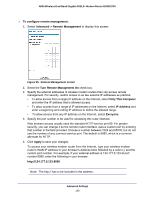
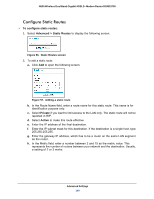
N600 Wireless Dual Band Gigabit ADSL2+ Modem Router DGND3700 Static Routes Static routes provide additional routing information to your router. Under normal circumstances, the router has adequate routing information after it has been configured for Internet access, and you do not need to configure additional static routes. You have to configure static routes only for unusual cases such as multiple routers or multiple IP subnets located on your network. Static Route Example As an example of when a static route is needed, consider the following case: • Your primary Internet access is through a cable modem to an ISP. • You have an ISDN router on your home network for connecting to the company where you are employed. This router's address on your LAN is 192.168.0.100. • Your company's network address is 134.177.0.0. When you first configured your router, two implicit static routes were created. A default route was created with your ISP as the wireless modem router, and a second static route was created to your local network for all 192.168.0.x addresses. With this configuration, if you attempt to access a device on the 134.177.0.0 network, your router forwards your request to the ISP. The ISP forwards your request to the company where you are employed, and the request is likely to be denied by the company's firewall. In this case you have to define a static route, telling your router that 134.177.0.0 should be accessed through the ISDN router at 192.168.0.100. The static route setup would look like Figure 57, Adding a static route. In this example: • The Destination IP Address and IP Subnet Mask fields specify that this static route applies to all 134.177.x.x addresses. • The Gateway IP Address field specifies that all traffic for these addresses are to be forwarded to the ISDN router at 192.168.0.100. • The value in the Metric field represents the number of routers between your network and the destination. This is a direct connection, so it can be set to the minimum value of 2. • The Private check box is selected only as a precautionary security measure in case RIP is activated. Advanced Settings 139