Netgear FSM726v3 FSM726v3 Hardware Installation Guide - Page 25
Troubleshooting, Troubleshooting Chart
 |
View all Netgear FSM726v3 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 25 highlights
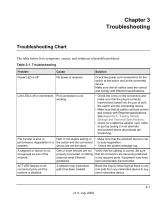
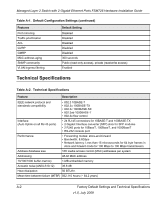
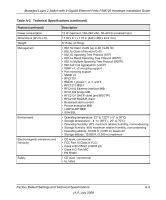
Chapter 3 Troubleshooting Troubleshooting Chart The table below lists symptoms, causes, and solutions of possible problems. Table 3-1. Troubleshooting Problem Cause Solution Power LED is off. No power is received Link LED is off or intermittent. Port connection is not working. Check the power cord connections for the switch at the switch and at the connected device. Make sure that all cables used are correct and comply with Ethernet specifications. • Check the crimp on the connectors and make sure that the plug is correctly inserted and locked into the port at both the switch and the connecting device. • Make sure that all cables used are correct and comply with Ethernet specifications. See Appendix A, "Factory Default Settings and Technical Specifications. • Check for a defective adapter card, cable, or port by testing it in an alternate environment where all products are functioning. File transfer is slow or Half- or full-duplex setting on • Make sure that the attached device is set performance degradation is a the switch and the connected to auto-negotiation. problem. device are not the same. • Check the system message log. A segment or device is not recognized as part of the network. One or more devices are not Verify that the cabling is correct. Be sure properly connected, or cabling that all connectors are securely positioned does not meet Ethernet in the required ports. Equipment may have guidelines. been accidentally disconnected. ACT LED flashes on all connected ports and the network is disabled. A network loop (redundant path) has been created. Break the loop by ensuring that there is only one path from any networked device to any other networked device. 3-1 v1.0, July 2009