2002 Ford Thunderbird Owner's Manual - Page 132
2002 Ford Thunderbird Manual
Page 132 highlights
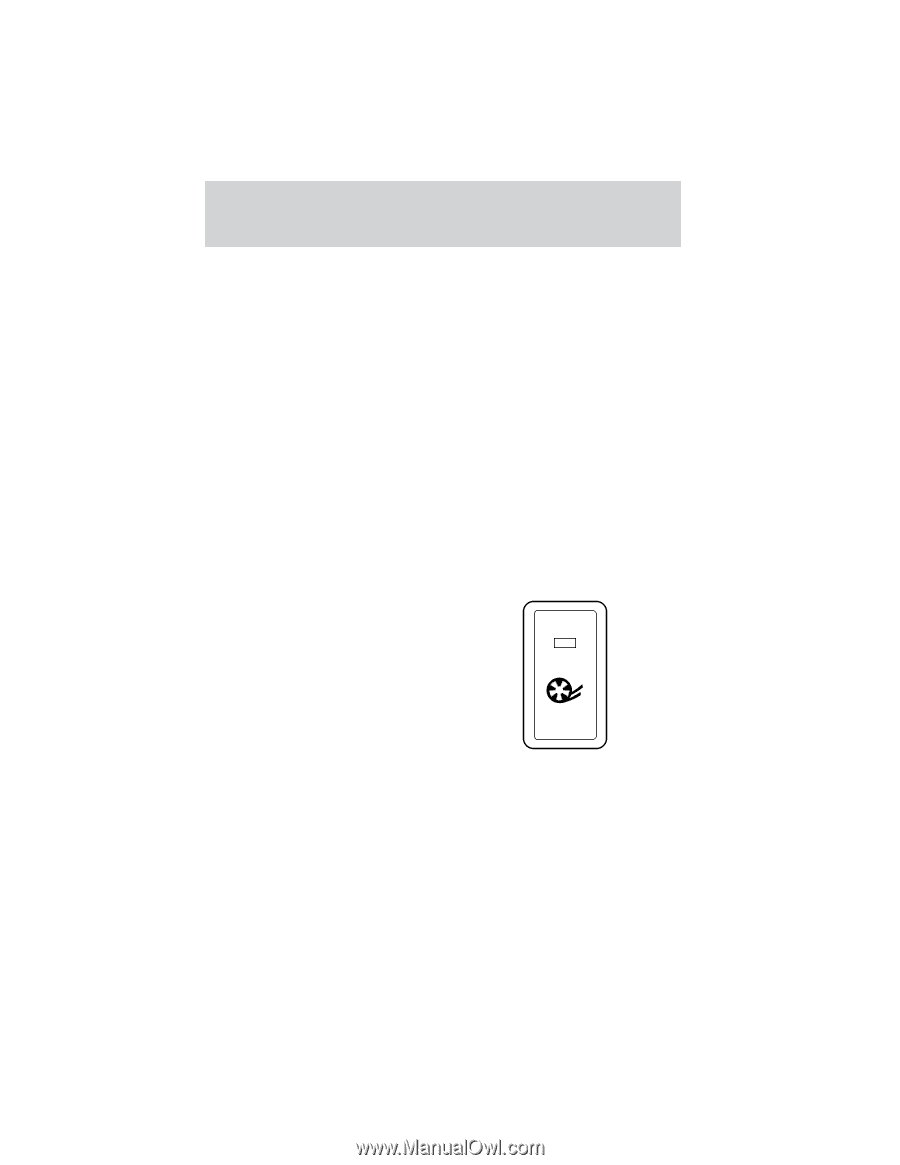
Driving controlling wheel spin. The system borrows many of the electronic and mechanical elements already present in the anti-lock braking system (ABS). Wheel-speed sensors allow excess rear wheel spin to be detected by the Traction Control portion of the ABS computer. Any excessive wheel spin is controlled by automatically applying and releasing the rear brakes in conjunction with engine torque reductions. Engine torque reduction is realized via the fully electronic spark and fuel injection systems. This process is very sensitive to driving conditions and very fast acting. The rear wheels "search" for optimum traction several times a second and adjustments are made accordingly. The Traction Control system will allow your vehicle to make better use of available traction on slippery surfaces. The system is a driver aid which makes your vehicle easier to handle primarily on snow and ice covered roads. This is especially evident if wheel spin-up should occur while turning. During Traction Control operation you may hear an electric motor type of sound coming from the engine compartment and the engine will not "rev-up" when you push further on the accelerator. This is normal system behavior. If you should become stuck in snow or on a very slippery road surface, try switching the Traction Control system off using the traction control OFF switch located on the left-hand side of the instrument panel. This may allow excess wheel spin to "dig" the vehicle out or enable a successful TRAC "rocking" maneuver. If the Traction Control system is cycled excessively, the brake portion of the system will shut down to prevent the rear brakes from overheating. A limited Traction Control function using only engine torque reduction will still help control wheels from over-spinning. When the rear brakes have cooled down, the system will again function normally. Anti-lock braking is not affected by this condition and will function normally during the cool down period. 132