Autodesk 25501-050008-1600A User Guide
Autodesk 25501-050008-1600A - REVIT STRUCT ESSN Manual
 |
UPC - 606121667650
View all Autodesk 25501-050008-1600A manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Autodesk 25501-050008-1600A manual content summary:
- Autodesk 25501-050008-1600A | User Guide - Page 1
REVIT® STRUCTURE Coordination between Revit Structure and Revit Architecture Structural engineers who use Revit® Structure software can better coordinate their work with architects using Revit® Architecture software. This paper examines how building information is shared between Revit Structure and - Autodesk 25501-050008-1600A | User Guide - Page 2
should be deleted since they can directly be copied from the architectural model. If a default project template with is used, the engineer manually deletes levels from the elevation view. The architectural model is then imported (File >> Import/Link), and the engineer identifies the architect's RVT - Autodesk 25501-050008-1600A | User Guide - Page 3
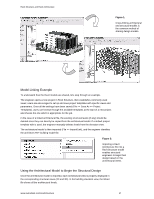
Revit Structure and Revit Architecture The engineer can visualize the architectural model in 3D (View >> New >> Default 3D view). The engineer's main interests are: the building levels; grids lines to layout the columns and structural framing; and the position of architectural columns (used to place - Autodesk 25501-050008-1600A | User Guide - Page 4
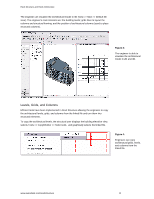
Revit Structure and Revit Architecture Additionally, the Options button lets the user offset the levels during this process to account for thickness of the floor finishes that are not needed on structural levels. Figure 5: Revit Structure allows users to automatically offset copied levels. It's - Autodesk 25501-050008-1600A | User Guide - Page 5
Revit Structure and Revit Architecture Figure 6: Revit Structure depicts columns going from higher levels to lower levels. The Copy tool from the design bar, allow users to transform the levels in the architectural linked file into structural levels for the structural floors. The engineer checks - Autodesk 25501-050008-1600A | User Guide - Page 6
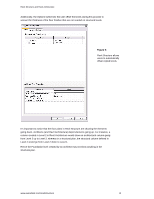
Revit Structure and Revit Architecture Figure 8: Structural floor plans can be created from the architectural floor plans. Browsing each floor plan, the user now sees the corresponding linked architectural floor. Levels (such as "structural floor") can be renamed in the project browser and - Autodesk 25501-050008-1600A | User Guide - Page 7
objects that the architect originally put in his design are preserved intact in the architectural file. The architect does not need to update them manually according to engineer's final design. While he links the Revit Structure file to his model, he can just turn off the visibility of the - Autodesk 25501-050008-1600A | User Guide - Page 8
Revit Structure and Revit Architecture Sharing the Same Revit Model In some situations, structural engineering firms using Revit Structure may want to share the same RVT file with architects using Revit Architecture software (versus cross-linking RVT files). For instance, if the architect and the - Autodesk 25501-050008-1600A | User Guide - Page 9
Revit Structure and Revit Architecture Similarly, the architectural team works on their own collection of architectural worksets. The project model is shared dynamically between users - each user contributing their own skill set when appropriate. Team members adding elements to worksets do not work - Autodesk 25501-050008-1600A | User Guide - Page 10
Revit Structure and Revit Architecture Coordination Between Engineers and Architects Since Revit Architecture and Revit Structure are based on the same platform, they include "monitoring" tools to ensure that model changes are coordinated. If the architect (using Revit Architecture) makes changes in - Autodesk 25501-050008-1600A | User Guide - Page 11
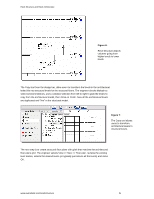
Revit Structure and Revit Architecture The next time an updated architectural file is reloaded into Revit Structure, the structural engineer selects Tools >> Coordination Review >> Select Link, clicks on the linked file and views the coordination review table. The coordination review tool is an - Autodesk 25501-050008-1600A | User Guide - Page 12
Revit Structure and Revit Architecture Interference Checking Structural engineers using Revit Structure and architects using Revit Architecture can perform interference checks between architectural and structural objects (or just between structural objects, or between any model objects). - Autodesk 25501-050008-1600A | User Guide - Page 13
Revit Structure and Revit Architecture If any detection is found, the report review will indicate the exact location of the problem. Figure 17: A structural column is interfering with a staircase. To see the element that is intersected or overlapping others, the user selects the element name in - Autodesk 25501-050008-1600A | User Guide - Page 14
Revit Structure, and Revit® MEP built on the Revit platform are complete, discipline-specific building design and documentation systems supporting all phases of design and construction documentation. From conceptual studies through the most detailed construction drawings and schedules, applications

REVIT
®
STRUCTURE
Coordination between
Revit Structure and
Revit Architecture
Structural engineers who use Revit
®
Structure
software can better coordinate their work with
architects using Revit
®
Architecture software. This
paper examines how building information is
shared between Revit Structure and Revit
Architecture users.
Linking Revit Models
Traditional structural processes begin with the architectural drawings, usually CAD-based
drawings. But structural engineers that are using Revit Structure and are working with
architects using Revit Architecture can
directly
link to the architectural Revit Architecture
file to start their structural design. Sharing the same building information model with
architects enables the structural and the architectural design and documentation to stay
coordinated.
Linking a Revit Architecture file with the Revit Structure model gives structural engineers a
starting point for their design, based on the architect's design intent. Changes made by
the architect can be tracked - facilitating design coordination and change management.
Similarly, architects using Revit Architecture can link a Revit Structure model into their
architectural models and reap the same coordination benefits.
Because both software solutions are using the same underlying building database, the
engineer can view, access, and query all the architectural properties of the model and the
architect can do the same for the structural elements.
Linking Models
Cross-linking the architectural and structural models is the preferred means of sharing the
models between architects and engineers if both are using Revit-based applications, but
are in separate organizations without access to a shared network. They can exchange
and cross-link their respective models, much like an architectural DWG file might be x-
referenced into a structural DWG file, but with far more intelligence.
Even when the engineers and architects are within the same A/E firm, linked files may still
be the preferred way of working - because they develop their respective designs at a
different pace and prefer the flexibility of keeping their own RVT files.
CONTENTS
Linking
Revit Models
.............
1
Sharing the Same
Revit Model
...............
8
Coordination
Monitor
....................
10
Interference
Checking
.................
12