Autodesk 25501-050008-1600A User Guide - Page 1
Autodesk 25501-050008-1600A - REVIT STRUCT ESSN Manual
 |
UPC - 606121667650
View all Autodesk 25501-050008-1600A manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 1 highlights
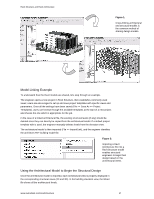
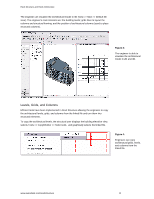
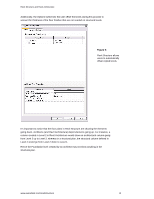
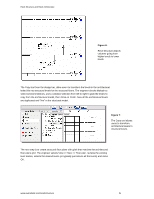
REVIT® STRUCTURE Coordination between Revit Structure and Revit Architecture Structural engineers who use Revit® Structure software can better coordinate their work with architects using Revit® Architecture software. This paper examines how building information is shared between Revit Structure and Revit Architecture users. CONTENTS Linking Revit Models 1 Sharing the Same Revit Model 8 Coordination Monitor 10 Interference Checking 12 Linking Revit Models Traditional structural processes begin with the architectural drawings, usually CAD-based drawings. But structural engineers that are using Revit Structure and are working with architects using Revit Architecture can directly link to the architectural Revit Architecture file to start their structural design. Sharing the same building information model with architects enables the structural and the architectural design and documentation to stay coordinated. Linking a Revit Architecture file with the Revit Structure model gives structural engineers a starting point for their design, based on the architect's design intent. Changes made by the architect can be tracked - facilitating design coordination and change management. Similarly, architects using Revit Architecture can link a Revit Structure model into their architectural models and reap the same coordination benefits. Because both software solutions are using the same underlying building database, the engineer can view, access, and query all the architectural properties of the model and the architect can do the same for the structural elements. Linking Models Cross-linking the architectural and structural models is the preferred means of sharing the models between architects and engineers if both are using Revit-based applications, but are in separate organizations without access to a shared network. They can exchange and cross-link their respective models, much like an architectural DWG file might be xreferenced into a structural DWG file, but with far more intelligence. Even when the engineers and architects are within the same A/E firm, linked files may still be the preferred way of working - because they develop their respective designs at a different pace and prefer the flexibility of keeping their own RVT files.