Compaq 307560-001 Compaq ProLiant 2500 Server Technology - Page 15
Slots, Host Bus, Processors, Memory, PCI Bus, EISA Bus
 |
UPC - 743172470379
View all Compaq 307560-001 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 15 highlights
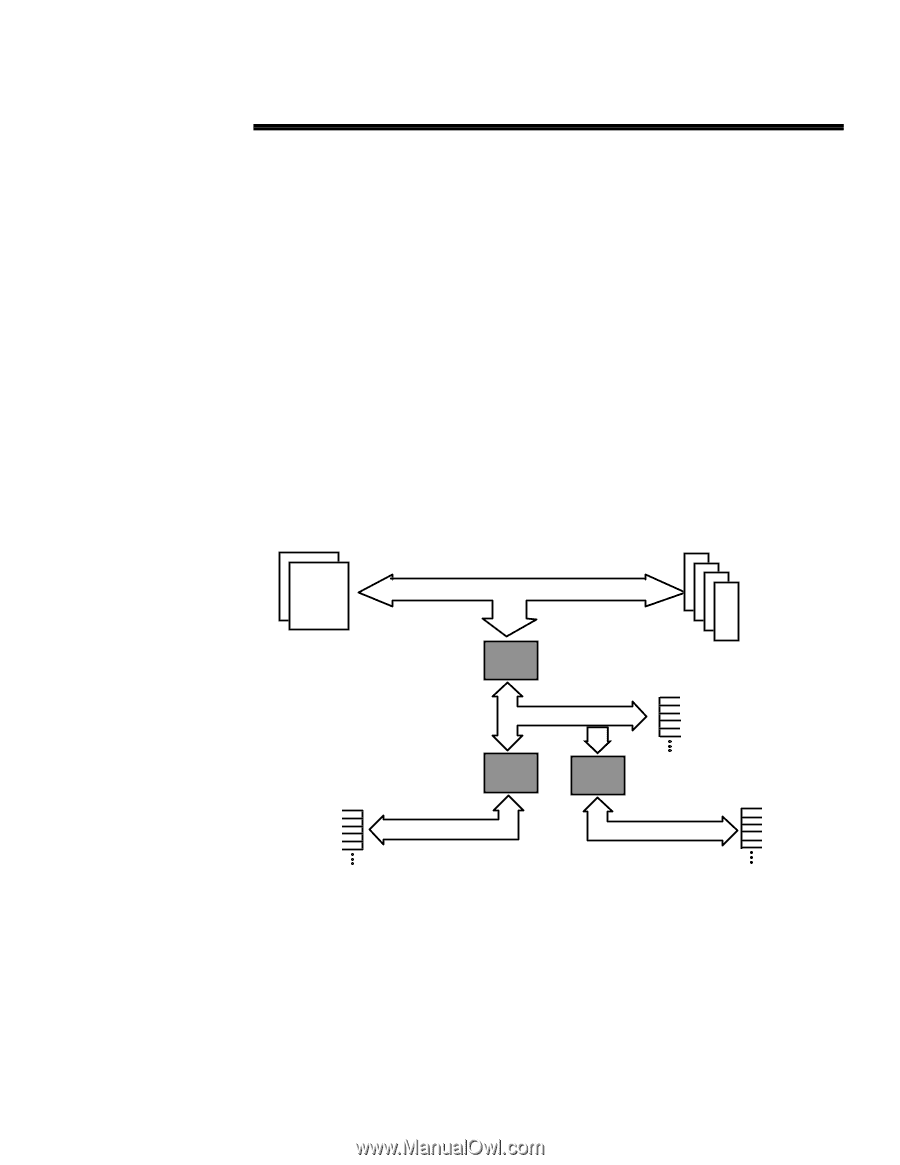
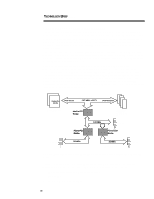
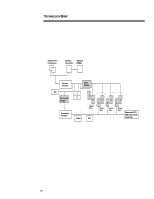
201A/1196 TECHNOLOGY BRIEF (cont.) ... PROLIANT 2500 SYSTEM ARCHITECTURE The overall goal of Compaq multiprocessing architecture is to maximize system throughput by allowing each critical server subsystem (processor, memory, and I/O) to operate as fast as reliably possible. Compaq chose to optimize the ProLiant 2500 for PCI, the new industry standard for I/O, while maintaining backward compatibility with EISA peripherals customers have previously purchased. Each subsystem in the ProLiant 2500 is individually optimized using separate, highbandwidth buses. The ProLiant 2500 Pentium Pro system features a Gunning Transceiver Logic (GTL+) processor bus (referred to in this brief as the host bus) that supports high-speed, low voltage transfers. It is a 64-bit split-transaction bus operating at 66 MHz with a throughput capacity of 267 megabytes per second. Data integrity is ECC protected. Figure 11 is a block diagram showing the PCI-to-PCI bridge architecture used in the ProLiant 2500. This primary bus expansion scheme is an economical choice for departmental servers and provides extra PCI slots for additional PCI devices. This expansion scheme supports one primary PCI bus directly and independently linked to the high speed Pentium Pro processor bus via a host-to-PCI bridge. A secondary PCI bus with the same 133 megabytes-per-second transfer rate is bridged off the primary bus. For backward compatibility, the ProLiant 2500 architecture includes an EISA bus also bridged off the Primary PCI bus. This EISA bus has a data transfer rate of 33 megabytes per second. Pentium Pro 200 Mhz 64-Bit Host Bus Host Bus (267 MB/s + ECC) 64-Bit Memory Bus Processors Host-to-PCI Bridge PCI Bus 131333MMB//ss EDO DIMMs Memory Slots 133 MB/s Slots PCI-to-PCI Bridge 133 MB/s PCI Bus PCI-to-EISA Bridge 33 MB/s EISA Bus Slots Figure 11. Block diagram showing the PCI-to-PCI bridge architecture used in the Compaq ProLiant 2500 Server. Figure 12 also depicts the I/O buses (primary and secondary PCI buses and EISA bus) and expansion slots in the ProLiant 2500. The primary PCI bus supports the following: • PCI on dedicated slots 5 and 6 and on shared slot 4 • EISA bridge • Integrated Remote Console (IRC) 15