D-Link DGS-1500-52 User Manual - Page 77
SNMP > SNMP > SNMP Global Settings, Port Link Up/Link Down
 |
View all D-Link DGS-1500-52 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 77 highlights
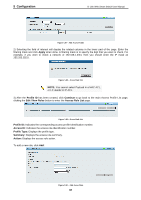
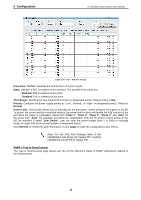
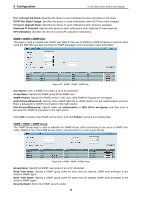
5 Configuration D-Link Web Smart Switch User Manual Figure 5.95 - SNMP > Trap to SmartConsole Destination IP: Specifies the destination IP. Illegal Login: Specifies the device to send illegal login notifications. Device Bootup: Specifies the device to send bootup notifications. Port Link Up/Link Down: Specifies the device to send notifications when port linkup or link down. RSTP Port State Change: Specifies the device to send notifications when RSTP port state changes. Firmware Upgrade State: Specifies the device to send notifications when firmware upgrades. Duplicate IP Detected: Specifies the device to send notifications when duplicate IP were detected. CPU Utilization: Specifies the device to send CPU utilization notifications. SNMP > SNMP > SNMP Global Settings Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) is an OSI Layer 7 (Application Layer) protocol designed specifically for managing and monitoring network devices. SNMP enables network management stations to read and modify the settings of gateways, routers, switches, and other network devices. Use SNMP to configure system features for proper operation, monitor performance and detect potential problems in the Switch or LAN. Managed devices that support SNMP include software (referred to as an agent), which runs locally on the device. A defined set of variables (managed objects) is maintained by the SNMP agent and used to manage the device. These objects are defined in a Management Information Base (MIB), which provides a standard presentation of the information controlled by the on-board SNMP agent. SNMP defines both the format of the MIB specifications and the protocol used to access this information over the network. The default SNMP global state is disabled. Select Enable and select Trap Settings then click Apply to enable the SNMP function. Figure 5.96 - SNMP > SNMP > SNMP Global Settings Trap Settings: Specifies whether the device can send SNMP notifications. SNMP Authentication Traps: Specifies the device to send authentication failure notifications. Device Bootup: Specifies the device to send bootup notifications. 71