Dell PowerEdge M915 Technical Guide - Page 21
ENERGY STAR Compliance, Thermal
 |
View all Dell PowerEdge M915 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 21 highlights
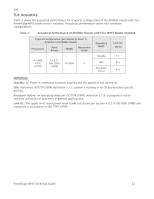
Dell Storage Altitude Operating Storage Airborne contaminant level Half sine shock on all six sides of 71G +/- 5% with a pulse duration of 2ms +/- 10% -15.2m to 3048m (-50 to 10,000ft) Note: For altitudes above 2950ft, the maximum temperature is derated 1°F/550ft -16 to 10,600m (-50 to 35,000ft) Class G1 or lower as defined by ISA-S71.04-1985 (G1 maximum corrosive contaminant levels measured at ≤ 50% relative humidity) 5.4 ENERGY STAR Compliance ENERGY STAR® qualified configurations can be accessed from the ENERGY STAR Compliance results landing page on Dell.com. 5.5 Thermal The Dell™ PowerEdge™ M915 is the first blade to support ≥130W processors in a 4-socket configuration. Larger heat sinks provide increased cooling capability, which enables 4-socket 140W configurations without restrictions on external ambient temperature. The M915 thermal solution includes the following features: Optimized airflow impedance for individual blade and chassis-level airflow balancing Custom top cover air baffling prevents DIMM airflow bypass to balance airflow and maintain proper DIMM cooling Custom-designed heat sinks maintain processor and chipset temperatures within thermal design targets Highly optimized fan control algorithm: o Base fan speeds are a function of hardware configuration and ambient temperature to minimize airflow for a given environment o PID fan control algorithms are used for processors, DIMMs, and NDC I/O thermal sensors to maintain appropriate thermal margin while minimizing component overcooling o NDC I/O sensor algorithm allows for lower fan speeds by sensing the air temperature near the exhaust of the blade while maintaining proper airflow and cooling for the mezzanine cards o The highest fan-speed request from the above algorithms is used to set the appropriate fan speed for the blade o The ambient and hardware configuration sets the minimum fan speed-other algorithms increase fan speed as needed to maintain proper cooling PowerEdge M915 Technical Guide 21