Dell S5248F-ON EMC Networking Virtualization Overlay with BGP EVPN - Page 9
Overlay networks
 |
View all Dell S5248F-ON manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 9 highlights
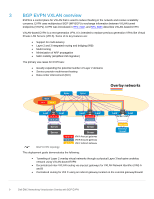
3 BGP EVPN VXLAN overview EVPN is a control plane for VXLAN that is used to reduce flooding in the network and resolve scalability concerns. EVPN uses multiprotocol BGP (MP-BGP) to exchange information between VXLAN tunnel endpoints (VTEPs). EVPN was introduced in RFC 7432, and RFC 8365 describes VXLAN-based EVPN. VXLAN-based EVPN is a next-generation VPN. It is intended to replace previous generation VPNs like Virtual Private LAN Service (VPLS). Some of its key features are: • Support for multi-tenancy • Layer 2 and 3 integrated routing and bridging (IRB) • Multi-homing • Minimization of ARP propagation • MAC mobility (simplified VM migration) The primary use cases for EVPN are: • Greatly expanding the potential number of Layer 2 domains • Service provider multi-tenant hosting • Data center interconnect (DCI) VNI B VNI A VNI C Spine Spine Overlay networks VTE P Leaf VLT Leaf VNI A GW VNI B GW VTE P Leaf VLT Leaf VNI A GW VNI B GW Server Server Server BGP EVPN topology Server VNI A GW VNI B GW VNI C GW VNI A Anycast gateway VNI B Anycast gateway VNI C Indirect gateway This deployment guide demonstrates the following: VTE P Leaf VLT Leaf Border Leafs VNI C GW Gateway/ Firewall • Tunneling of Layer 2 overlay virtual networks through a physical Layer 3 leaf-spine underlay network using VXLAN-based EVPN • Decentralized inter-VXLAN routing via anycast gateways for VXLAN Network Identifier (VNI) A and B • Centralized routing for VNI C using an indirect gateway located on the external gateway/firewall 9 Dell EMC Networking Virtualization Overlay with BGP EVPN