Gigabyte B550M S2H User Manual - Page 37
Appendix, 3-1 Configuring a RAID Set
 |
View all Gigabyte B550M S2H manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 37 highlights
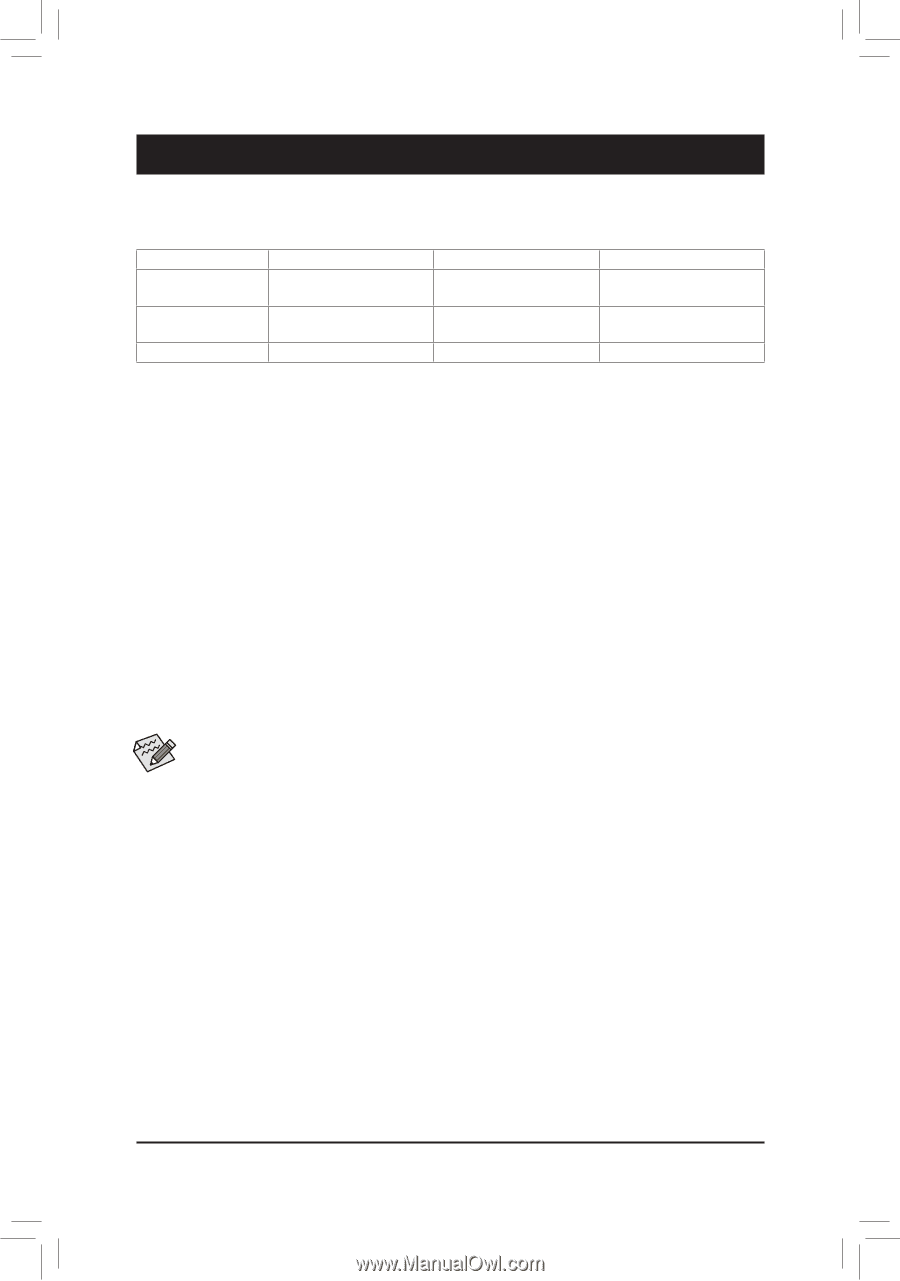
Chapter 3 Appendix 3-1 Configuring a RAID Set RAID Levels RAID 0 Minimum Number of Hard Drives ≥2 Array Capacity Number of hard drives * Size of the smallest drive Fault Tolerance No RAID 1 RAID 10 2 4 Size of the smallest drive (Number of hard drives/2) * Size of the smallest drive Yes Yes Before you begin, please prepare the following items: •• At least two SATA hard drives or SSDs. (Note) (To ensure optimal performance, it is recommended that you use two hard drives with identical model and capacity). •• Windows setup disc. •• Motherboard driver disc. •• A USB thumb drive. Configuring the Onboard SATA Controller A. Installing SATA hard drive(s) in your computer Install the hard drives/SSDs in the SATA/M.2 connectors on the motherboard. Then connect the power connectors from your power supply to the hard drives. B. Configuring SATA controller mode in BIOS Setup Make sure to configure the SATA controller mode correctly in system BIOS Setup. Steps: Turn on your computer and press to enter BIOS Setup during the POST (Power-On Self-Test). Under Settings\IO Ports, set SATA Configuration\SATA Mode to RAID. Then save the settings and restart your computer. (If you want to use NVMe PCIe SSDs to configure RAID, make sure to set NVMe RAID mode to Enabled.) The BIOS Setup menus described in this section may differ from the exact settings for your motherboard. The actual BIOS Setup menu options you will see shall depend on the motherboard you have and the BIOS version. C. UEFI RAID Configuration Steps: 1. In BIOS Setup, go to Boot and set CSM Support to Disabled. Save the changes and exit BIOS Setup. 2. After the system reboot, enter BIOS Setup again. Then enter the Settings\IO Ports\RAIDXpert2 Configuration Utility sub-menu. 3. On the RAIDXpert2 Configuration Utility screen, press on Array Management to enter the Create Array screen. Then, select a RAID level. RAID levels supported include RAID 0, RAID 1, and RAID 10 (the selections available depend on the number of the hard drives being installed). Next, press on Select Physical Disks to enter the Select Physical Disks screen. 4. On the Select Physical Disks screen, select the hard drives to be included in the RAID array and set them to Enabled. Next, use the down arrow key to move to Apply Changes and press . Then return to the previous screen and set the Select CacheTagSize, Read Cache Policy and Write Cache Policy. 5. Move to Create Array and press to begin. 6. After completing, you'll be brought back to the Array Management screen. Under Manage Array Properties you can see the new RAID volume and information on RAID level, array name, array capacity, etc. (Note) An M.2 PCIe SSD cannot be used to set up a RAID set either with an M.2 SATA SSD or a SATA hard drive. - 37 -