HP 6120G/XG HP ProCurve Series 6120 Blade Switches IPv6 Configuration Guide - Page 95
Router Access and Default Router Selection, Router Advertisements, Router Solicitations
 |
View all HP 6120G/XG manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 95 highlights
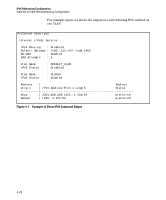
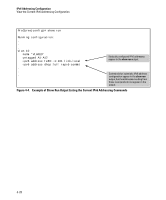
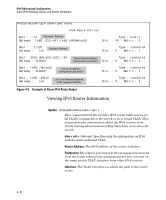
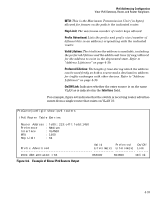
IPv6 Addressing Configuration Router Access and Default Router Selection Router Access and Default Router Selection Routing traffic between destinations on different VLANs configured on the switch or to a destination on an off-switch VLAN is done by placing the switch on the same VLAN interface or subnet as an IPv6-capable router configured to route traffic to other IPv6 interfaces or to tunnel IPv6 traffic across an IPv4 network. Router Advertisements An IPv6 router periodically transmits router advertisements (RAs) on the VLANs to which it belongs to notify other devices of its presence. The switch uses these advertisements for purposes such as: ■ learning the MAC and link-local addresses of IPv6 routers on the VLAN (For devices other than routers, the switch must use neighbor discovery to learn these addresses.) ■ building a list of default (reachable) routers, along with router lifetime and prefix lifetime data ■ learning the prefixes and the valid and preferred lifetimes to use for stateless (autoconfigured) global unicast addresses (This is required for autoconfiguration of global unicast IPv6 addresses.) ■ learning the hop limit for traffic leaving the VLAN interface ■ learning the MTU (Maximum Transmission Unit) to apply to frames intended to be routed Router Solicitations When an IPv6 interface becomes operational on the switch, a router solicita tion is automatically sent to trigger a router advertisement (RA) from any IPv6 routers reachable on the VLAN. (Router solicitations are sent to the AllRouters multicast address; ff02::2. Refer to "Multicast Application to IPv6 Addressing" on page 3-21.) If an RA is not received within one second of sending the initial router solicitation, the switch sends up to three additional solicitations at intervals of four seconds. If an RA is received, the sending router is added to the switch's default router list and the switch stops sending router solicitations. If an RA is not received, then IPv6 traffic on that VLAN cannot be routed, and the only usable unicast IPv6 address on the VLAN is the link-local address. 4-29