HP 6120G/XG HP ProCurve Series 6120 Blade Switches Advanced Traffic Management - Page 186
Classifiers for Prioritizing Outbound Packets, Packet Classifiers and Evaluation Order, Note On Using
 |
View all HP 6120G/XG manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 186 highlights
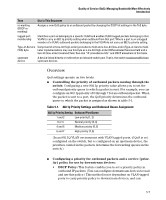
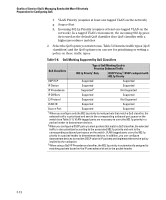
Quality of Service (QoS): Managing Bandwidth More Effectively Introduction Classifiers for Prioritizing Outbound Packets Note On Using Multiple Criteria ProCurve recommends that you configure a minimum number of the available QoS classifiers for prioritizing any given packet type. Increasing the number of active classifier options for a packet type increases the complexity of the possible outcomes and consumes switch resources. Packet Classifiers and Evaluation Order The switches covered in this guide provide six QoS classifiers (packet criteria) you can use to configure QoS priority. Table 5-4. Classifier Search Order and Precedence Search Precedence QoS Classifier Type Order 1 1 (highest) UDP/TCP Application Type (port) 2 2 Device Priority (destination or source IP address) 3 3 IP Type of Service (ToS) field (IP packets only) 4 4 Protocol Priority (IP, IPX, ARP, AppleTalk, SNA, and NetBeui) 5 5 VLAN Priority 6 6 Incoming source-port on the switch 7 7 (lowest) Incoming 802.1p priority (This default value is present in tagged VLAN environments) Where multiple classifier types are configured, a switch uses the highest-tolowest search order shown in table 5-4 to identify the highest-precedence classifier to apply to any given packet. When a match between a packet and a classifier is found, the switch applies the QoS policy configured for that classifier and the packet is handled accordingly. Note that on the switches covered in this guide, if the switch is configured with multiple classifiers that address the same packet, the switch uses only the QoS configuration for the QoS classifier that has the highest precedence. In this case, the QoS configuration for another, lower-precedence classifier that may apply is ignored. For example, if QoS assigns high priority to packets belonging to VLAN 100, but normal priority to all IP protocol packets, since protocol priority (4) has precedence over VLAN priority (5), IP protocol packets on VLAN 100 will be set to normal priority. 5-10