HP D2200sb Serial Attached SCSI technology, 3rd edition - Page 14
Zoning methodology, Zone management, Advanced Enterprise, Features Enable Next Generation SAS Systems
 |
View all HP D2200sb manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 14 highlights
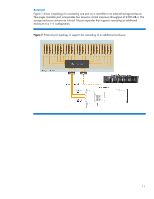
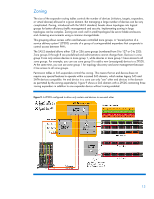
Zoning methodology Zoning uses the unique ID number of each expander PHY to provide a secure method of managing SAS devices. Zoning assigns each port of a zoning expander to a zone group, and any device attached to one of the ports becomes part of that respective zone group. By default, all devices within a zone group can interact with each other. The permission table in the expander controls access between devices in different zone groups. If an attached device changes, you may configure the expander to set the zone group to 0 (no access), which allows an address-resolved-like policy to be implemented. For example, if a particular SAS device needs to have certain permissions, move the device to a different expander in the fabric, then you can reprogram the zone group at the new location. Zoning, as originally introduced by the T10 standards group, had PHY-resolved and address-resolved versions. The address-resolved version is not currently used. You can read more about the two types of zoning in this SCSI Trade Association document, "Advanced Enterprise Features Enable Next Generation SAS Systems". Zone management The zone manager, a SAS-2 compliant software mechanism, lets you configure and manage each zone. As shown in Figure 10 (top), the zone manager can control a zone by using an end device with a SAS port connected to one of the zoning expanders. The zone manager can also control a zone through a sideband interface (such as Ethernet) on one or more zoning expanders (Figure 10 bottom). Figure 10. Direct zone management using an end device (top), or using a sideband interface to connect directly to expanders (bottom) 14