HP Evo D500 Comparison of Intel Pentium III and Pentium 4 Processor Performanc - Page 11
Streaming Single Instruction Multiple Data Extension 2 SSE2 with 144 new instructions
 |
View all HP Evo D500 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 11 highlights
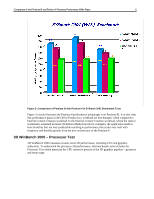
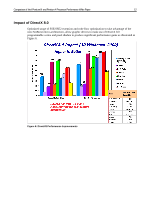
Comparison of Intel Pentium III and Pentium 4 Processor Performance White Paper 11 • Advanced Dynamic Execution with very wide windows of instructions (126 instructions versus 42 instructions in the Pentium III) from which the execution units can choose to execute, thus avoiding dependency stalls that would prevent execution units from doing useful work. In addition, 4KB of branch target buffer (as compared to 1KB in the Pentium III), and a multilevel advanced branch prediction algorithm to keep detail on the history of past program branches, thus reducing by approximately 33% the mis-predictions rate as compared to the Pentium III. • 400 MHz System Bus with enhancements to signaling scheme and bus protocols, thus featuring data bandwidth and bus transfer efficiencies much higher than those of the Pentium III, as follows: - 200% data bandwidth improvement (3.2GB/s (8 bytes x 400 Mtransfers/s) versus 1.06 GB/s (8 bytes x 133 Mtransfers/s)) - 17% latency improvement for first critical data read - 46% latency improvement for 64-byte read - 25% latency improvement for data write - 64% latency improvement for 64-byte write - New cycles every two clocks at 200 MHz versus every three clocks at 133 MHz - 200% snoop bandwidth improvement (3.2GB/s (64 bytes/2 clocks @ 100 MHz) versus 1.06GB/s (32 bytes/4clocks @ 133 MHz)). - Higher concurrent requests - Faster interrupt servicing (bus message versus I/O cycles) • Streaming Single Instruction Multiple Data Extension 2 (SSE2) with 144 new instructions that deliver 128-bit SIMD integer arithmetic operation and 128-bit SIMD Double-Precision Floating Point to reduce the number of instructions to complete a task or program, effectively increasing IPCs.