HP Evo D500 Comparison of Intel Pentium III and Pentium 4 Processor Performanc - Page 3
Introduction, Comparison of Pentium 4 and Pentium III Architecture, Benefits
 |
View all HP Evo D500 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 3 highlights
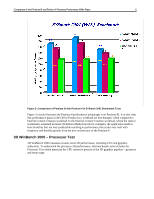
Comparison of Intel Pentium III and Pentium 4 Processor Performance White Paper 3 Introduction This White Paper provides information useful in understanding the differences between the Intel® Pentium® 4 processor and the previous-generation Pentium III. A discussion is included about the architectural differences in the two processors and the performance benefits they provide. When evaluating performance, there is no single performance test ("benchmark") that can completely describe the performance of a complex system like modern microprocessor or personal computer. It is important to obtain the complete performance picture. In other words, the system should deliver high performance across the entire spectrum of applications such as productivity, multimedia, 3D and Internet. Each of these application categories caries a unique set of computation and data movement characteristics; thus it is important to realize how each class of application would benefit or not from the new architecture. It is also important to realize the investment protection delivered, where the new architecture will provide reasonable performance gain for current applications while providing headroom for future growth as more and more ISVs will fully take advantage of the new architecture. With that in mind, it is expected that there is a non-uniform gain in performance, as each class of current application lends itself more to the new architecture while others do not. Using the Compaq Deskpro EN platform equipped with 1 GHz Pentium III processor as the baseline, benchmark results of the new Compaq Evo D500 platform equipped with the 1.7 GHz Pentium 4 processor are presented as a comparison of the two architectures. Comparison of Pentium 4 and Pentium III Architecture Benefits As Internet and digital media become more pervasive in modern computing, the Pentium 4 processor is optimized for a new level of digital audio, video, photography and 3D performance. For corporate users, the Pentium 4 offers excellent performance with added headroom for future applications such as • Java technology and XML, which will be increasingly enabled in Office XP, Windows® XP and Web services • Enhanced 3D rendering for business analysis, video decompression for e-learning, and peerto-peer interaction for improved collaboration • Secure connections with support for latest encryption technology for data transfer and eCommerce transactions. How are these potential enhancements possible with this new processor? Let's explore the microarchitecture enhancements in the Pentium 4 processor: Representing a breakthrough to a new level of computing, the Pentium 4 processor is a completely redesigned version of the earlier Intel IA32 processor architecture or Pentium III while maintaining backward compatibility with existing applications. This means the Pentium 4 processor protects user's current investment in existing applications while providing new optimized instructions, registers, and data structures for future applications.