HP ML115 The AMD processor roadmap for industry-standard servers, 6th edition - Page 3
AMD64 technology, Instruction set and registers
 |
UPC - 884962252765
View all HP ML115 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 3 highlights
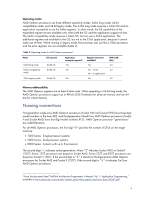
Table 1. 32-bit x86 instructions common to AMD processors Instruction name Standard x86 Description Instructions for logical and arithmetic operations, address calculations, and has 16-bit index registers for memory pointers Register type GPR Size of registers 32-bit Number of registers 8 MMX Multimedia instructions that allow the processor to do 64-bit MMX 64-bit 8 SIMD operations x87 Instructions for floating point calculations FP 80-bit* 8 SSE, SSE2, SSE3, and SSE4a SSE improved upon the MMX instructions and allowed processors to do 128-bit SIMD floating-point operations. SSE2 added 64-bit parallel floating point numeric support. It also added new instructions to support 128-bit SIMD integer operations. SSE3 instructions include 13 instructions that accelerate performance of SSE technology, SSE2 technology, and x87-floating-point math capabilities. SSE4a instructions include two new SSE instructions. SSE4a instructions also add support for unaligned SSE loadoperation, which formerly required 16-byte alignment. MMX 128-bit 8 * According to the article "An Introduction to 64-bit Computing and x86-64" by Jon Stokes1, the "x87 uses 80-bit registers to do double-precision floating point. The floats themselves are 64-bit, but the processor converts them to an internal, 80-bit format for increased precision when doing computations." AMD Opteron processors support the AMD 3Dnow!™ instruction set, AMD's version of multimedia instructions. The 3DNow! set added SIMD instructions to improve the vector-processing (floating point) performance of graphic-intensive and multimedia applications. AMD64 technology Introduced in 2003, AMD64 technology is the AMD microarchitecture and instruction set that provides full support for 64-bit operating systems and applications. The most important feature of AMD64 is support for very large virtual and physical memory in a flat address space. Instruction set and registers AMD64 instructions can take advantage of the 64-bit wide registers in AMD Opteron processors. These registers are used by the applications only when running the processors in 64-bit long mode. To support the AMD64 instructions, the registers expand to include the following: • Eight new 64-bit GPRs • Extensions of the eight original, 32-bit GPRs to 64 bits • Eight new 128-bit registers for SSE, SSE2, and SSE3 instructions 1 Available at http://arstechnica.com/cpu/03q1/x86-64/x86-64-1.html 3