HP ProLiant DL590/64 ProLiant DL590/64 Server Technology - Page 5
Pentium II Xeon and Pentium III Xeon processors., cont.,
 |
View all HP ProLiant DL590/64 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 5 highlights
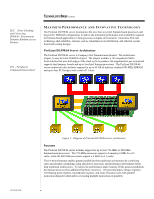
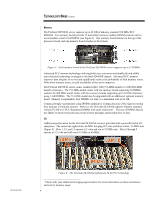
TC020702TB TECHNOLOGY BRIEF (cont.) ... In addition, the floating point performance of Itanium processors is significantly better than that of today's IA-32 processors. The Itanium processor has two extended-precision and two single-precision floating point units, capable of executing up to four extended-precision or eight single-precision floating point operations per clock cycle. The Itanium processor uses a high-performance architecture, Explicitly Parallel Instruction Computing (EPIC), which is based on very long instruction word (VLIW) systems. This architecture achieves a new level of parallelism. New parallel-processing features include: • Hardware support for multiple parallel data streams • Fewer memory latencies than traditional architectures • Better anticipation of instruction streams that can be made parallel • Support of more parallel streams • A third level of caching • Making data parallel before it enters the microprocessor Because the Itanium processor has the resources to support more registers, functional units, logic, instructions, cache, and data, it delivers increased processing power. It also links the program compilers more closely to the processor for more efficient execution of parallel instructions and optimized application performance. Current IA-32 processors, on the other hand, exclusively use hardware within the processor to decide which instructions can be executed simultaneously. The Itanium processor uses a new instruction set designed for optimal performance with the EPIC architecture. The Itanium processor is also capable of executing IA-32 (x86) instructions, so it accommodates the transition from IA-32 environments to IA-64 environments. While running an IA-32 application, the processor is switched to an IA-32 mode. When the user returns to the 64-bit OS or launches an IA-64 application, the processor is switched back to IA-64 mode. For IA-32 applications running under a 64-bit OS that supports IA-32 applications and drivers, the OS manages the processor mode switching. While some 32-bit software is compatible with the Itanium processor, applications achieve higher performance when they are ported to 64-bit versions. Itanium processors are installed in sockets on the motherboard. A new physical form factor (Figure 2) provides four times the bandwidth of the 330-contact slot connector design used in Pentium II Xeon and Pentium III Xeon processors. Figure 2: The Itanium processor uses a new physical form factor. 5