HP ProLiant DL590/64 ProLiant DL590/64 Server Technology - Page 8
Distributed Power System, cont., Compaq designed the ProLiant DL590/64 server's I/O board.
 |
View all HP ProLiant DL590/64 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 8 highlights
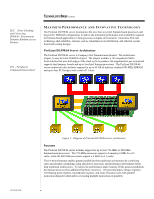
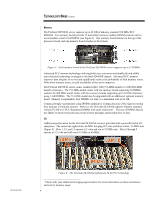
TC020702TB TECHNOLOGY BRIEF (cont.) ... Figure 6: Compaq designed the ProLiant DL590/64 server's I/O board. Distributed Power System Historically, most ProLiant servers have been powered by one or more AC-to-DC, multiple output power supplies. Power from the power supplies is cabled or routed to all components of the server. This is known as centralized power distribution. This approach works well at moderate power levels. But as server performance has increased, so has the demand for more power. To manage the increased power, the ProLiant DL590/64 server uses a hot-pluggable distributed power system that is fully redundant, including the high-line AC line feeds. In a distributed power system, a primary power supply converts power from the AC mains to an intermediate DC voltage that is easy to distribute throughout a server system. A common value is +48 volts DC, which is a level high enough to keep the currents low but within the safe voltage limits. At the load, a second power supply converts the high voltage to the required lower voltage. In the ProLiant DL590/64 server, these local power converters are known as system power modules. Throughout the industry, they are also known as point of load converters or voltage regulator modules (VRMs). Since the system power modules are located next to the loads, the large cables and wires typical with high currents are no longer required. This allows a significant cost saving and a simpler design. System power modules are typically more reliable than the power supplies they replace. Three 1250-watt primary power supplies in the front of the ProLiant DL590/64 server take in AC power. Each of these distributes 48 volts DC at up to 1200 watts (see Figure 7). These 48-volt supplies provide power to the processor power modules and to the memory boards. They also provide 48 volts to the three system power modules that convert the power into the 3.3 and 5-volts needed for PCI slots and logic and into the 12 volts needed for the server's fans and hard drives. 8