HP StorageWorks 6000 HP StorageWorks VLS and D2D Solutions Guide (AG306-96028, - Page 96
Mapping Configuration, Add Target Appliance, as if configuring a replication target
 |
View all HP StorageWorks 6000 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 96 highlights
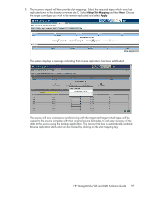
of reverse replication is the same as if initializing the device at the remote site and so depends on the link speed and amount of critical data to be reverse replicated. Once the server is recovered and able to perform backups again, configure replication back to the target device in the data center all over again. This option is easy to implement even in many-to-one replication scenarios. Reverse replication is a means whereby the source and target libraries maintain their identity, but where at the point of rebuilding the source using a special "recover first" mode to force the source to go to the target and reverse replicate data from the target back to the source. The basic process takes place entirely from the remote site where the new D2D appliance has been installed: 1. With a new replacement D2D at the remote site set the appropriate network settings. 2. Create an identical virtual library (or libraries if more than one was originally configured). 3. At the source select the Replication tab from the GUI. Then select Mapping Configuration. Begin as if configuring a replication target, but start the recovery wizard instead of the replication wizard. 4. Now create a new target appliance. Select Add Target Appliance. The IP address of the target appliance (which still exists) is entered and when found the target appliance is shown. Then select Next. If there are multiple target libraries within the target appliance select the relevant one that was configured prior to the disaster at remote site C. 96 D2D Systems