HP Xw460c Remote Graphics Software 5.3.0 User Guide - Page 11
Introduction to HP Remote Graphics Software
 |
View all HP Xw460c manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 11 highlights
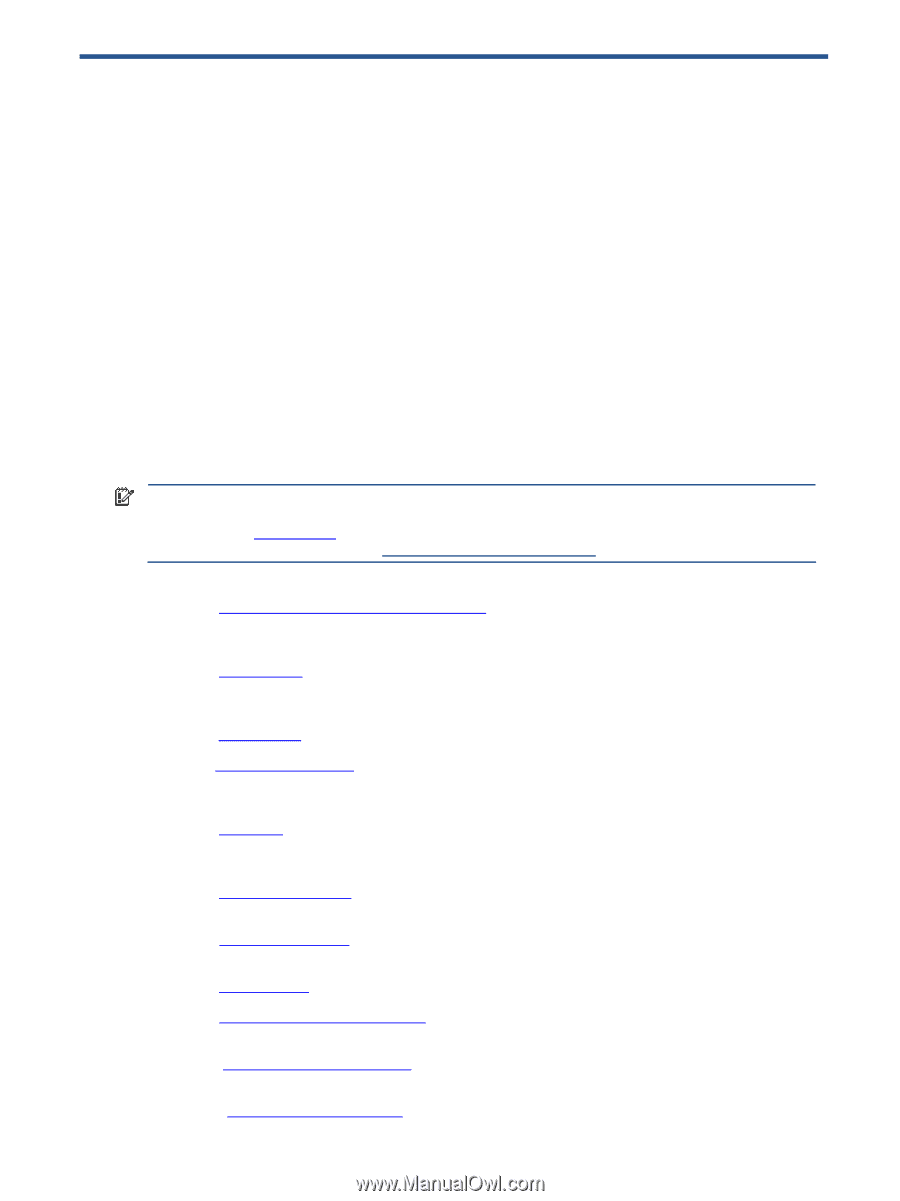
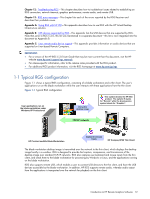
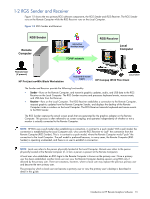
1 Introduction to HP Remote Graphics Software This guide provides information that you will need to install, configure, and use HP Remote Graphics Software (RGS). RGS enables you to view and interact with the desktop of a remote computer over a standard TCP/IP computer network. HP Remote Graphics Software (RGS) is a high-performance remote desktop connection protocol that delivers an exceptional remote desktop user experience for rich user environments that include video, web flash animations and graphics intensive applications. All applications run natively on the remote system and take full advantage of the compute and hardware graphics resources of the sending system. HP RGS captures the desktop of the remote system and transmits it over a standard network to a window on a local client using advanced image compression technology specifically designed for text, digital imagery and high frame rate video applications. A local hardware keyboard and mouse is supported as well as USB device redirection to provide an interactive, high performance, multi-display desktop experience. HP RGS supports a broad range of client virtualization technologies including multi-user virtual desktop infrastructure (VDI) solutions, blade PCs, blade workstations, desktop PCs, mobile PCs and workstations. IMPORTANT: Beginning at RGS 5.2.0, HP implemented licensing for the RGS Sender. The RGS Receiver remains a free download, and can be used on any number of computers. For an overview of RGS licensing, see Section 2-3, "RGS licensing." For detailed information on RGS licensing, see the HP Remote Graphics Software Licensing Guide, available at www.hp.com/support/rgs_manuals. This guide is organized as follows: Chapter 1: Introduction to HP Remote Graphics Software-This chapter provides an introduction to RGS, describing a typical RGS configuration, and the roles of the Local and Remote Computers. This chapter also describes the primary features of RGS. Chapter 2: RGS overview-This chapter gives an overview of the RGS capabilities, including the supported computers and operating systems, RGS connection topologies, multi-monitor configurations, licensing information, remote USB, and remote audio. Chapter 3: Installing RGS-Installation of the RGS Sender and Receiver is described in this chapter. Chapter 4: Pre-connection checklist-Establishing an RGS connection from a Receiver to a Sender requires that the Local and Remote Computers be in the correct state. This chapter provides a checklist of items that should be verified before attempting an RGS connection. Chapter 5: Using RGS-This chapter describes how to use RGS. Establishing a connection from the Local Computer to the Remote Computer in Normal Mode is described, including the different login methods. Features such as collaboration are also described. Chapter 6: Advanced capabilities-This chapter describes the RGS advanced capabilities that are provided by each of the tabs in the Receiver Control Panel. Chapter 7: Using Directory Mode-Establishing RGS connections using Directory Mode is described in this chapter. Chapter 8: RGS properties-This chapter describes each of the RGS Sender and Receiver properties. Chapter 9: Sender event logging on Windows-This chapter describes the Windows event logging capability of RGS. Chapter 10: Remote Application Termination-This chapter describes how the Windows event logging capability of RGS can be used to terminate applications if a desktop session is left running without supervision. Chapter 11: Optimizing RGS performance-This chapter provides a number of suggestions to optimize RGS performance. Introduction to HP Remote Graphics Software 11