HP t5550 Windows CE 6.0 Administrator's Guide HP Thin Client t5540 and t5550 B - Page 55
Network and Dial-up Connections, Dial-up Connection, Virtual Private Network (PPTP) Connection - thin client case
 |
View all HP t5550 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 55 highlights
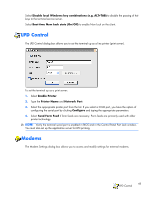
Network and Dial-up Connections The Network and Dial-up Connections window allows you to configure connectivity between the terminal and the Internet, a network, or a computer. To make a new connection, double-click the Make New Connection icon, select the type of connection you want to make, and then configure the connection. Choose from the following connection types: ● Dial-up Connection ● Direct Connection ● VPN (PPTP) ● VPN (L2TP) ● Ethernet (PPPoE) Dial-up Connection You can use a dial-up modem with the thin client to access a dial-up server. This method provides two ways to access the enterprise intranet: ● An enterprise dial-up server connects directly to the enterprise intranet. ● An Internet Service Provider (ISP) dial-up server provides access to the Internet, from which the thin client must access an enterprise Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol (PPTP) Virtual Private Network (VPN) server that connects to the enterprise intranet. NOTE: The dial-up server must be a Microsoft Remote Access Server or another server that supports industry-standard protocols. Direct Connection This type of connection allows you to connect directly to another computer through the serial port on the terminal. NOTE: This option is available only to thin clients with serial ports. Virtual Private Network (PPTP) Connection Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol (PPTP) is a network protocol that enables the secure transfer of data between a remote client (in this case the thin client) and an enterprise server environment by creating a VPN across TCP/IP-based data networks such as the Internet. It provides a password-protected path Network and Dial-up Connections 47