Intel DB43LD Product Specification - Page 32
System States and Power States
 |
View all Intel DB43LD manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 32 highlights
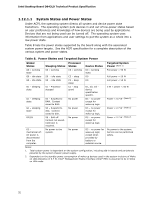
Intel Desktop Board DB43LD Technical Product Specification 1.12.1.1 System States and Power States Under ACPI, the operating system directs all system and device power state transitions. The operating system puts devices in and out of low-power states based on user preferences and knowledge of how devices are being used by applications. Devices that are not being used can be turned off. The operating system uses information from applications and user settings to put the system as a whole into a low-power state. Table 8 lists the power states supported by the board along with the associated system power targets. See the ACPI specification for a complete description of the various system and power states. Table 8. Power States and Targeted System Power Global States Processor Sleeping States States Device States Targeted System Power (Note 1) G0 - working state G0 - idle state G0 - idle state G1 - sleeping state G1 - sleeping state G1 - sleeping state G2/S5 G3 - mechanical off. AC power is disconnected from the computer. S0 - working S0 - idle state S0 - idle state S1 - Processor stopped S3 - Suspend to RAM. Context saved to RAM. S4 - Suspend to disk. Context saved to disk. S5 - Soft off. Context not saved. Cold boot is required. No power to the system. C0 - working C3 - sleep C4 - deep sleep C1 - stop grant No power No power No power No power D0 - working state. D0 D0 Full power > 50 W Full power < 50 W Full power < 50 W D1, D2, D3 - device specification specific. D3 - no power except for wake-up logic. D3 - no power except for wake-up logic. D3 - no power except for wake-up logic. 5 W < power < 50 W Power < 4.7 W (Note 2) Power < 2.7 W (Note 2) Power < 2.7 W (Note 2) D3 - no power for wake-up logic, except when provided by battery or external source. No power to the system. Service can be performed safely. Notes: 1. Total system power is dependent on the system configuration, including add-in boards and peripherals powered by the system chassis' power supply. 2. Dependent on the standby power consumption of wake-up devices used in the system inclusive of Wake on LAN allowance of 0.7 W. Intel® Management Engine Interface (Intel® MEI) is assumed to be in Wake on LAN mode. 32