Intel RS2WG160 Hardware User Guide - Page 34
Fault Tolerance, Electrical Characteristics, Table 9. Fault Tolerance Features
 |
View all Intel RS2WG160 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 34 highlights
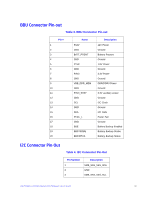
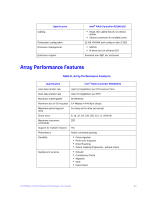
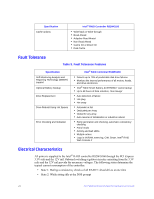
Specification Cache options Intel® RAID Controller RS2WG160 • Write-back or Write-through • Read Ahead • Adaptive Read Ahead • Non Read Ahead • Cache I/O or Direct I/O • Disk Cache Fault Tolerance Table 9. Fault Tolerance Features Specification Self Monitoring Analysis and Reporting Technology (SMART) support Optional Battery Backup Drive Replacement Drive Rebuild Using Hot Spares Error Checking and Indication Intel® RAID Controller RS2WG160 • Detects up to 70% of predictable disk drive failures • Monitors the internal performance of all motors, heads, and drive electronics. • Intel® RAID Smart Battery AXXRSBBU7 cache backup • Up to 48 hours of data retention, 'Gas Gauge' • Auto detection of failure • Hot-plug • Hot-swap • Automatic at fail • Dedicated per Array • Global for any array • Auto-resume of initialization or rebuild on reboot • Parity generation and checking, automatic consistency checking • Patrol reads • Activity and fault LEDs • Multiple retries • Logs in NVRAM, event log, CIM, Smart, Intel® RAID Web Console 2 Electrical Characteristics All power is supplied to the Intel® RAID controller RS2WG160 through the PCI Express 3.3V rails and the 12V rail. Onboard switching regulator circuitry operating from the 3.3V rails and the 12V rail provide the necessary voltages. The following states determine the typical current consumption of the controller: • State 1: During a consistency checks of all RAID 5 virtual drives at one time • State 2: While sitting idle at the DOS prompt 24 Intel® RAID Controller RS2WG160 Hardware User's Guide