Netgear RT338 RT338 Reference Manual - Page 30
Netgear RT338 Manual
 |
UPC - 606449004250
View all Netgear RT338 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 30 highlights
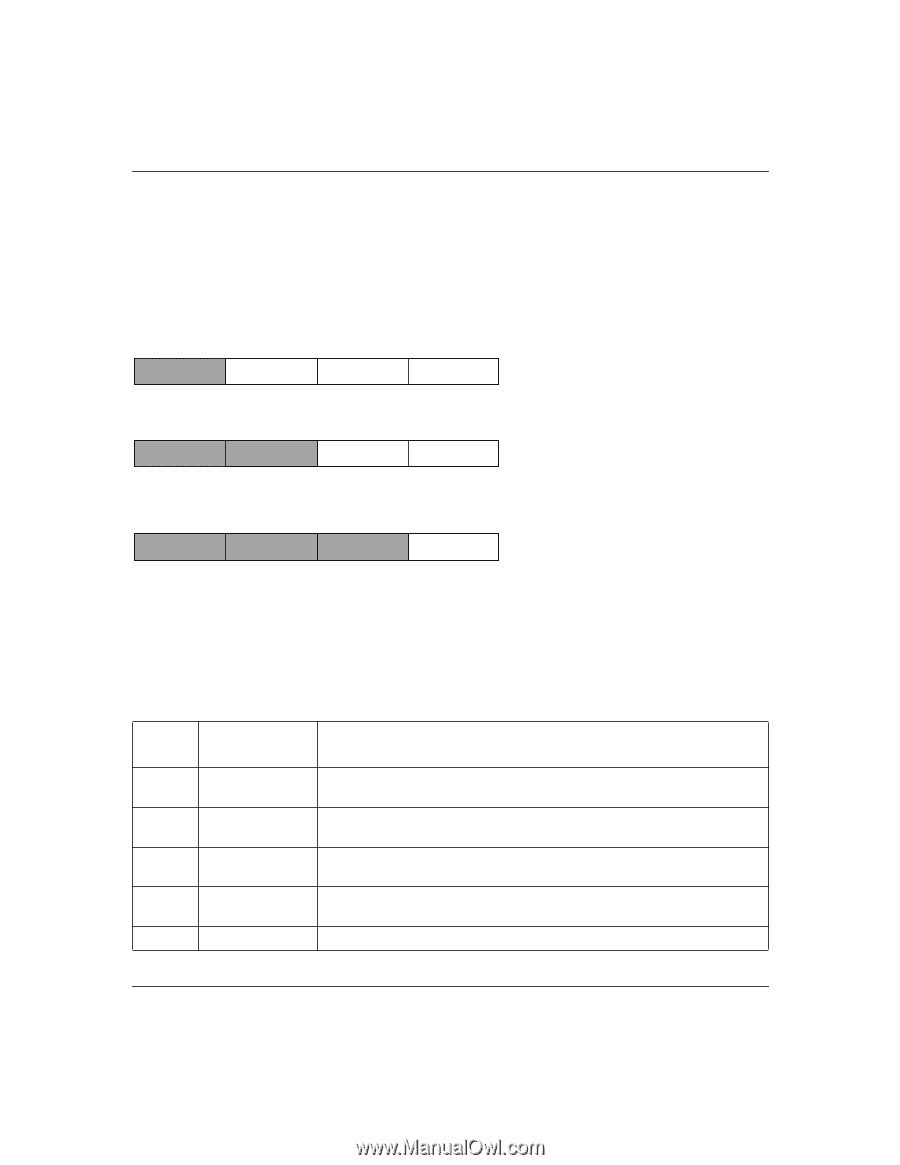
Reference Guide for the Model RT338 ISDN Router There are five standard classes of IP addresses. The address classes determine the network and host sections of the address differently. Address classes allow for different numbers of hosts on a network. Each address type begins with a unique bit pattern, which is used by the TCP/IP software to identify the address class. After the address class has been determined, the software can correctly identify the host section of the address. The three main address classes are illustrated in Figure 1-1, which shows the network and node sections of the address for each address type. Class A Network Class B Node Network Class C Node Figure 1-1. Network Node 7261 Three Main Address Classes IP address classes are described in Table 1-1. Table 1-1. Address Classes Address Class Range Description A 1.x.x.x to 126.x.x.x Class A addresses can have up to 16,777,214 hosts on a single network. They use an 8-bit network number and a 24-bit node number. B 128.1.x.x to Class B addresses can have up to 65,354 hosts on a network. They use a 191.254.x.x 16-bit network number and a 16-bit node number. C 192.0.1.x to Class C addresses can have 254 hosts on a network. They use 24 bits for 223.255.254.x the network address and 8 bits for the node. D 224.0.0.0 to Class D addresses are used for multicasts (messages sent to many hosts). 239.255.255.255 E Class E addresses are for experimental use. 1-8 Introduction