Ricoh Aficio MP C2050SPF Features Guide - Page 11
User Authentication, External
 |
View all Ricoh Aficio MP C2050SPF manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 11 highlights
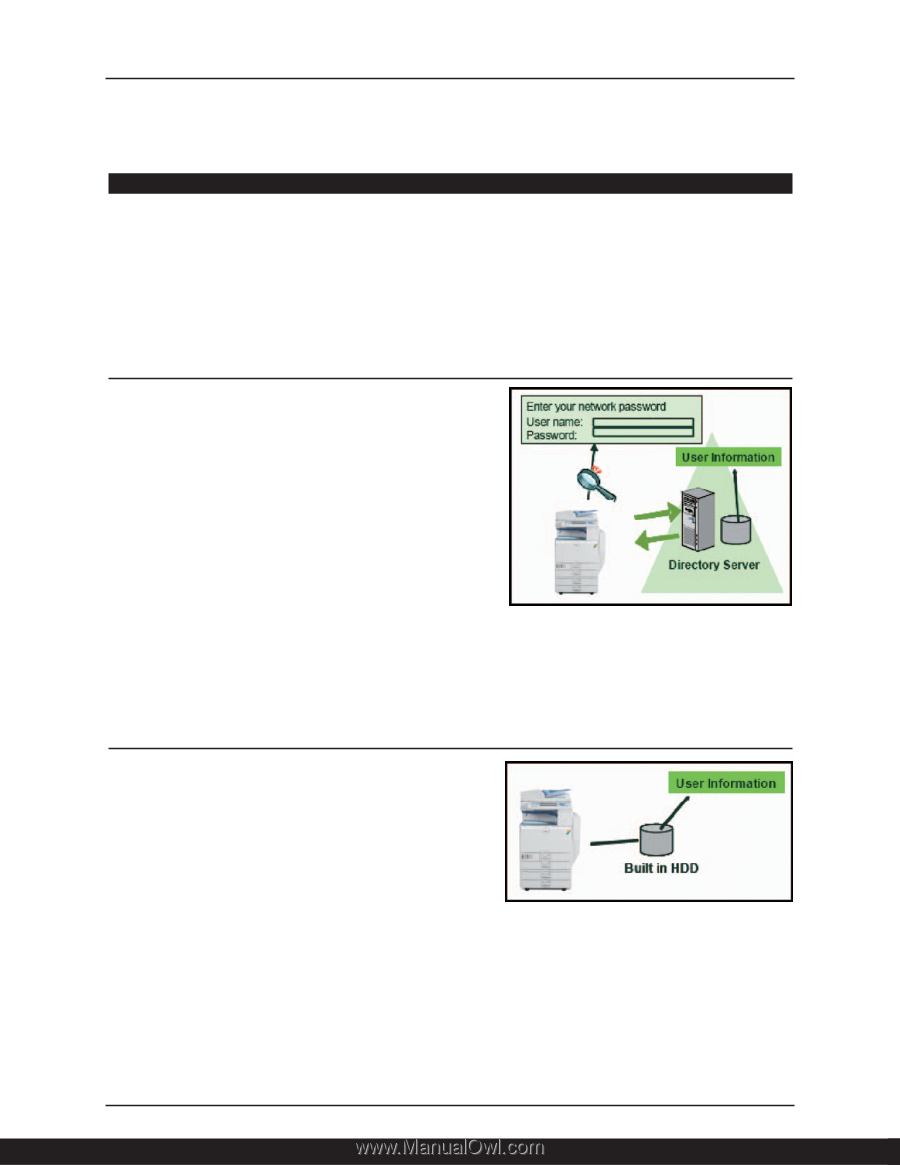
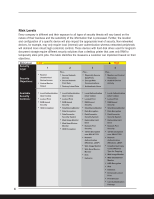
User Authentication Several modes of user authentication are available to ensure only authorized personnel issued a valid user name and password has access to the device and the data stored within it. There are two types of authentication, External, which uses information from a remote server to verify users, and Internal, which identifies users by data stored locally in the machine. As a result, the types of authentication available to users will vary based on how the device is installed, networked or a direct PC connection. In most cases a Hard Disk Drive on the target device is required to store the data needed for user authentication. External Authentication Modes ■ Windows Authentication: For customer networks using Microsoft Active Directory servers, this mode verifies the identity of the user by comparing login credentials (user name/password) against the database of authorized users on the Windows Network Server, thus granting or denying access to device functionality. Using the same data that matches other areas of user network access eliminates the need for users to remember multiple passwords, and for IT personnel to support another login-password system. Once access is granted, the user's name is automatically entered in the Sender's Name field of outgoing Scan-to-Email jobs, providing traceability by eliminating "From" field spoofing. ■ LDAP Authentication: Uses the company E-mail server to verify authorization in a manner similar to above, but for networks using a server other than Microsoft Active Directory. This mode permits or denies access to the entire device; it cannot control access to individual functions. Internal Authentication Modes ■ Basic Authentication: Limits device access by asking for a user name and password stored in the device's built-in address book. This allows customers to control device/data access in non-networked environments, and to limit access to stored files. No one without a valid user name/password can access the machine. ■ User Code Authentication: Utilizes Ricoh's standard User Code system to authenticate the user. The operator simply enters their User Code, which is compared to the registered data in the device's address book. No one without a valid User Code can access the machine. The same code can be used by multiple users to track system use by client, period, or by job for bill-back purposes, for example. 8