Seagate ST120FP0021 Seagate 600 Pro SSD Product Manual - Page 10
Physical Characteristics Access Time Time To Ready
 |
View all Seagate ST120FP0021 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 10 highlights
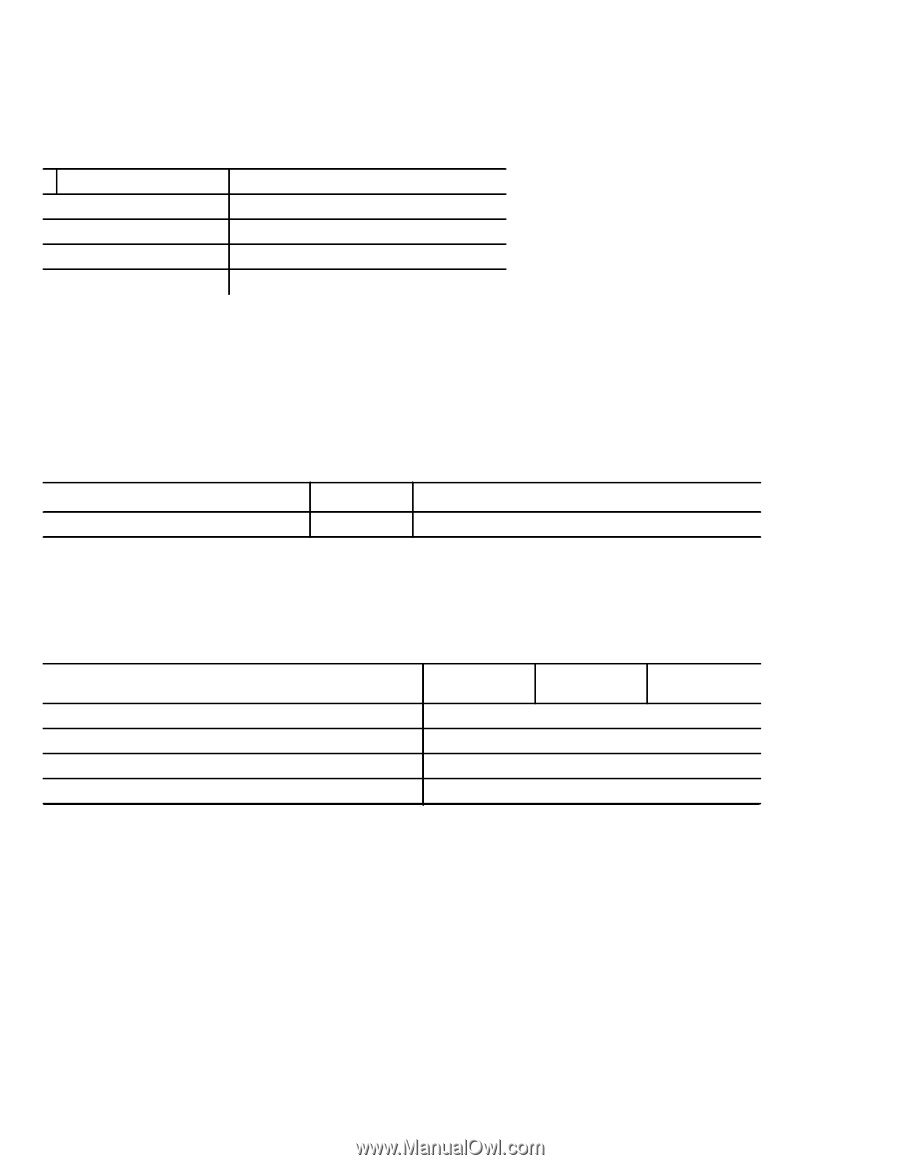
When evaluating performance of SSD devices, it is recommended to measure performance of the device in a method that resembles the targeted application using real world data and workloads. Test time should also be adequately large to ensure that sustainable metrics and measures are obtained. 2.5 PHYSICAL CHARACTERISTICS Maximum height Maximum width Maximum length Max weight 2.5" models 7.00 mm (0.276 in) 70.10 mm (2.760 in) 100.45 mm (3.955 in) 100 g (0.220 lb) 2.6 ACCESS TIME Access measurements are taken with nominal power at 25°C ambient temperature. All times are measured using drive diagnostics. The specifications in the table below are defined as follows: • Page-to-page access time is an average of all possible page-to-page accesses in both directions for a sequentially precon- ditioned drive. • Average access time is a true statistical random average of at least 5000 measurements of accesses between program- mable pages, less overhead, on a randomly preconditioned drive. *TYPICAL ACCESS TIMES (μs) Average READ 158 WRITE 125 Note. These drives are designed to provide the highest possible performance under typical conditions. However, due to the nature of Flash memory technologies there are many factors that can result in values different than those stated in this specification. 2.7 TIME TO READY Power-on to Ready for non-Media related Commands (sec) Power-on to Ready for Media related commands (sec) Standby to Ready (sec) Ready to power removal (sec) 480GB 400GB 3 (typ) 14 (max) 3 (max) 3 (max) 240GB 200GB 120GB 100GB Power-on to Ready for non-media related commands is defined as the time that it will take the drive to respond from the application power until it is ready to accept commands from the host that do not require access to the flash media. In some cases the drive may accept media access commands during this time, but the commands will not be completed or status returned to the host until the media can be accessed safely. Commands such as Check Power and Identify are examples of non-media related commands. Power-on to Ready for media related commands is defined as the time that it will take the drive to respond from the application power until it is ready to accept commands from the host that require access to the flash media. Commands such as FPDMA Read Extended and FPDMA Write Extended are examples of media related commands. This value includes the time needed to charge the Power Loss Data Protection Circuit to a level that is adequate to protect customer data from unexpected power loss. The maximum time for Power-on to Ready is dependent on if a STANDBY IMMEDIATE was issued prior to power down and the write workload profile prior to power down. SEAGATE 600 PRO SSD PRODUCT MANUAL, REV. B 6