Sharp LC42SB45UT LC-42SB45U LC-42SB45UT Operation Manual - Page 16
View Mode - changes inputs
 |
UPC - 074000371484
View all Sharp LC42SB45UT manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 16 highlights
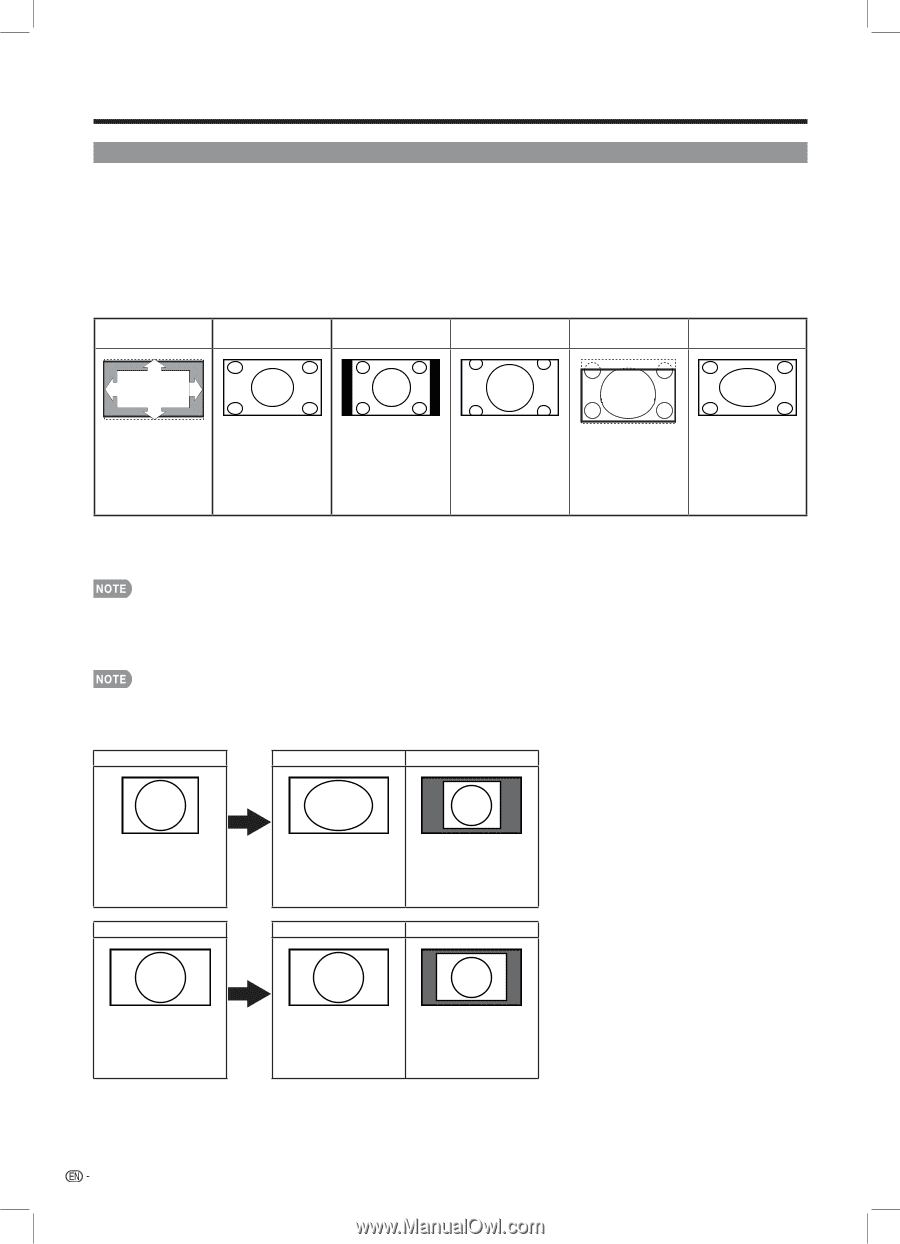
Direct Button Operation VIEW MODE You can select the screen size. 1 Press VIEW MODE. •• The View Mode menu displays. •• The menu lists the View Mode options selectable for the type of video signal currently being received. 2 Press VIEW MODE or a/b while the View Mode menu is displayed to select a desired item on the menu. •• You can sequentially select a View Mode that has its own aspect ratio. ■ For 4:3 programs Example: Screen size images Automatic S.Stretch (Smart stretch) Side Bar Zoom 16:9 Subtitle Stretch Suitable for viewing subtitles and enlarging picture automatically to fill the screen. Suitable for stretching 4:3 programs to fill the screen. Suitable for viewing conventional 4:3 programs in their normal format. Suitable for viewing wide-screen 2.35:1 anamorphic DVDs in full screen. Suitable for viewing 4:3 pictures and leaving the subtitle visible. This mode is useful for 1.78:1 DVDs. When viewing 1.85:1 DVDs, stretch mode will still show very thin black bands at the top and bottom of the screen. ■ For HD programs Stretch: Suitable for viewing wide-screen 1.78:1 aspect ratio program, stretch mode will still show very thin black bands at the top and bottom of the screen. •• When using Dot by Dot, it is possible to see noise or bars around different outer portions of the screen. Please change view mode to correct this. •• For HD-DTV programs, only "Automatic", "Smart Stretch", and "Stretch" modes can be selected. ■ For PC input mode ••Connect the PC before making adjustments. (See page 12.) •• Selectable screen size may vary with input signal type. Example: Screen size images Input signal Stretch Dot by Dot 4:3 Input signal An image fully fills the screen. Stretch Detects the resolution of the signal and displays an image with the same number of pixels on the screen. Dot by Dot 16:9 An image fully fills the Detects the resolution of screen. the signal and displays an image with the same number of pixels on the screen. 16