TRENDnet TE100-MP1U User's Guide - Page 38
Print Server in Unix/Linux - problems
 |
UPC - 710931204193
View all TRENDnet TE100-MP1U manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 38 highlights
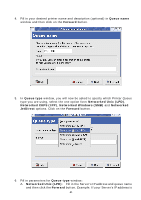
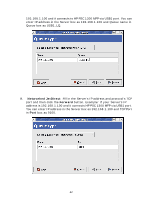
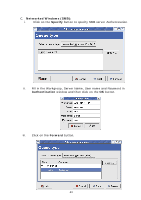
Chapter5 Print Server in Unix/Linux This chapter describes how to add network printers to Unix/Linux PC. Configuring Host File If using IP administration system like DNS, manually registering the Server Name and IP address may be not required. Otherwise, you have to edit hosts file and contact your network administrator. 1. Log in to Linux machine by "root". # login root 2. Register the Server's Server Name and IP address into /etc/hosts file. To edit host file, use an editor, e.g. "vi". Example: The IP address is "192.168.1.100", Server Name is "MP2U" 192.168.1.1 dns # DNS Server 192.168.1.2 mail # Mail Server 192.168.1.100 MP2U # Server 3. Switch on the Server. Verify the network connection by using the ping command. # ping MP2U If there is no response or error occurs, there may be problems with IP address configuration, host file editing or network status. Please contact your network administrator. Printing by LPD/LPR This section explains how to print using LPD protocol of TCP/IP. For further information on "lpr" and "lp" commands, refer to your workstation manual. LPD Protocol: LPD (Line Printer Daemon) is a protocol that enables you to execute printing to a printer on the network. Remote-Printer Queue: The Server has two remote printer queues: USB1_LQ and USB2_LQ with respect to USB port 1 and UB port2. To print files using a printer driver, use "lp" or "lpr". 5.3 Using the Server on BSD UNIX/Linux 1. Log in to the BSD Unix machine through "root". # login root 2. Register the Server into /etc/printcap file. Example: To register the printer of USB1 port by the printer name "Printer1". Printer1:\ ---(A) :lp=:rm=MP2U:rp=USB1_LQ:\ ---(B) 38