ZyXEL NBG334S User Guide - Page 105
enable NAT to use the Any IP feature on the NBG334W.
 |
View all ZyXEL NBG334S manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 105 highlights
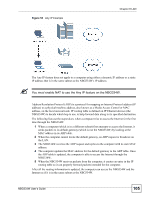
Figure 55 Any IP Example Chapter 8 LAN The Any IP feature does not apply to a computer using either a dynamic IP address or a static IP address that is in the same subnet as the NBG334W's IP address. " You must enable NAT to use the Any IP feature on the NBG334W. Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) is a protocol for mapping an Internet Protocol address (IP address) to a physical machine address, also known as a Media Access Control or MAC address, on the local area network. IP routing table is defined on IP Ethernet devices (the NBG334W) to decide which hop to use, to help forward data along to its specified destination. The following lists out the steps taken, when a computer tries to access the Internet for the first time through the NBG334W. 1 When a computer (which is in a different subnet) first attempts to access the Internet, it sends packets to its default gateway (which is not the NBG334W) by looking at the MAC address in its ARP table. 2 When the computer cannot locate the default gateway, an ARP request is broadcast on the LAN. 3 The NBG334W receives the ARP request and replies to the computer with its own MAC address. 4 The computer updates the MAC address for the default gateway to the ARP table. Once the ARP table is updated, the computer is able to access the Internet through the NBG334W. 5 When the NBG334W receives packets from the computer, it creates an entry in the IP routing table so it can properly forward packets intended for the computer. After all the routing information is updated, the computer can access the NBG334W and the Internet as if it is in the same subnet as the NBG334W. NBG334W User's Guide 105