Casio FX 2.0 User Guide - Page 11
Graph Functions
 |
UPC - 079767191139
View all Casio FX 2.0 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 11 highlights
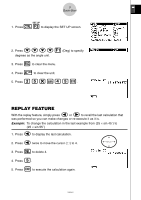
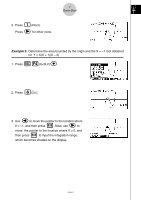
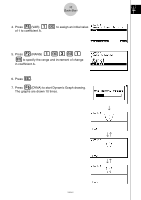
6 Quick-Start GRAPH FUNCTIONS The graphing capabilities of this calculator makes it possible to draw complex graphs using either rectangular coordinates (horizontal axis: x ; vertical axis: y) or polar coordinates (angle: θ ; distance from origin: r). All of the following graphing examples are performed starting from the calculator setup in effect immediately following a reset operation. Example 1: To graph Y = X(X + 1)(X - 2) m 1. Press . 2. Use defc to highlight w GRPH • TBL, and then press . 3. Input the formula. v (v+b) (v -c)w 5 w 4. Press (DRAW) or to draw the graph. Example 2: To determine the roots of Y = X(X + 1)(X - 2) 4 1. Press (G-SLV) to display the pull-up menu. 19990401

19990401
GRAPH FUNCTIONS
The graphing capabilities of this calculator makes it possible to draw complex graphs
using either rectangular coordinates (horizontal axis:
x
; vertical axis:
y
) or polar
coordinates (angle:
θ
; distance from origin:
r
).
All of the following graphing examples are performed starting from the calculator setup
in effect immediately following a reset operation.
Example
1:
To graph Y = X(X + 1)(X – 2)
1. Press
m
.
2. Use
defc
to highlight
GRPH
•
TBL
, and then press
w
.
3. Input the formula.
v
(
v
+b)
(
v
-c)
w
4. Press
5
(DRAW) or
w
to draw the graph.
Example
2:
To determine the roots of Y = X(X + 1)(X – 2)
1. Press
4
(G-SLV) to display the pull-up menu.
6
Quick-Start