Casio FX 2.0 User Guide - Page 12
Example
 |
UPC - 079767191139
View all Casio FX 2.0 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 12 highlights
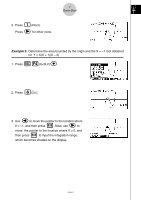
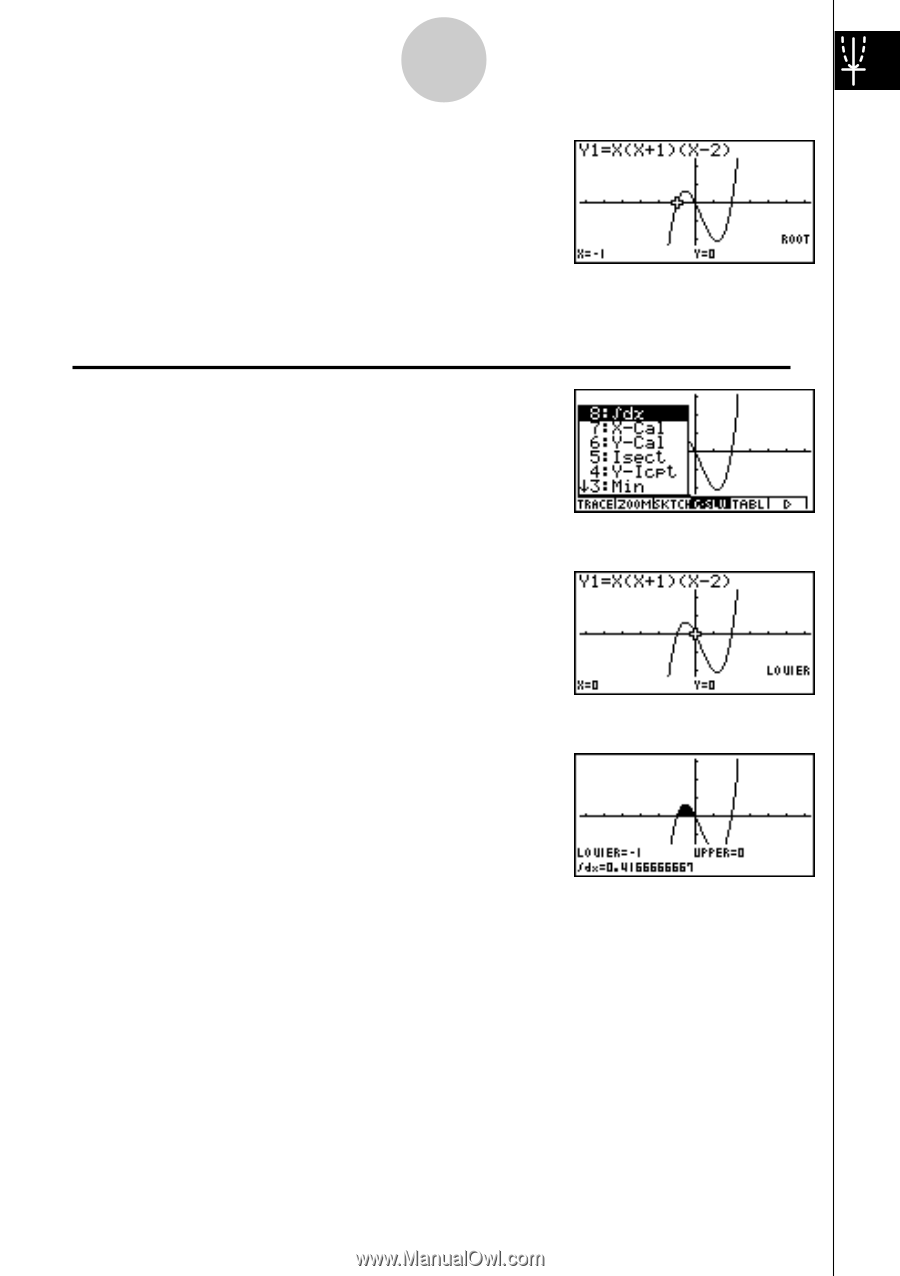
7 Quick-Start b 2. Press (Root). e Press for other roots. Example 3: Determine the area bounded by the origin and the X = -1 root obtained for Y = X(X + 1)(X - 2) 1. Press i4(G-SLV)c. i 2. Press (∫dx). d 3. Use to move the pointer to the location where w e X = -1, and then press . Next, use to move the pointer to the location where X = 0, and w then press to input the integration range, which becomes shaded on the display. 19990401
19990401
2. Press
b
(Root).
Press
e
for other roots.
Example
3:
Determine the area bounded by the origin and the X = –1 root obtained
for
Y = X(X + 1)(X – 2)
1. Press
i
4
(G-SLV)
c
.
2. Press
i
(
∫
dx
).
3. Use
d
to move the pointer to the location where
X = –1, and then press
w
. Next, use
e
to
move
the pointer to the location where X = 0, and
then press
w
to input the integration range,
which becomes shaded on the display.
7
Quick-Start