Compaq ProLiant 8000 Compaq ProLiant 8000 Server Technology - Page 5
Profusion Chipset, I/O Interface, Memory Interface, Processor Interface
 |
View all Compaq ProLiant 8000 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 5 highlights
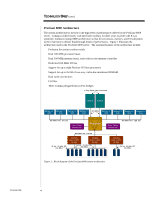
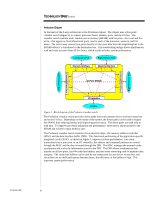
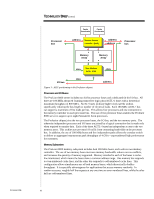
TC000603TB TECHNOLOGY BRIEF (cont.) ... Profusion Chipset At the heart of the 8-way architecture is the Profusion chipset. The chipset uses a five-point crossbar switch (Figure 2) to connect processor buses, memory ports, and the I/O bus. The crossbar switch contains static random access memory (SRAM) with ten ports-five read and five write-that appear as five bidirectional ports, one for each of the processor, memory, and I/O buses. The switch may connect two ports directly or may store data from the originating bus in the SRAM before it is transferred to the destination bus. This nonblocking design allows simultaneous read and write accesses from all five buses, which results in better system performance. Left Memory Port Right Memory Port Memory Interface Memory Interface 10-Port SRAM Processor Interface Right Processor Bus Processor Interface Left Processor Bus I/O Interface I/O Bus Figure 2: Block diagram of the Profusion crossbar switch. The Profusion crossbar switch provides direct paths from each memory bus to each processor bus and to the I/O bus. Depending on the status of the system, the direct paths can be used to bypass the SRAM, thus reducing latency and improving performance. The direct paths are used only to read data. To improve processor utilization and performance, write data is always posted to the SRAM and written to main memory later. The Profusion crossbar switch consists of two physical chips-the memory address controller (MAC) and the data interface buffer (DIB). This functional partitioning of the application-specific integrated circuit (ASIC), as shown in Figure 3, improves system performance. For every transaction from a processor or an I/O controller, the address and command portions are routed through the MAC and the data is routed through the DIB. The MAC manages the external cache accelerators and tracks the information stored in the DIB. The DIB allows simultaneous data transfer on all five ports, has 64-cache-line buffers, and uses error-correcting code to maintain data integrity. The cache-line buffers can be used by any transaction for any device on any bus; and since there are no dedicated queues between buses, the efficiency of the buffers is high. This improves system performance. 5