D-Link DGS-3100-24P Product Manual - Page 85
Default VLANs, VLAN and Trunk Groups, VLAN Status - 24
 |
UPC - 790069304941
View all D-Link DGS-3100-24P manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 85 highlights
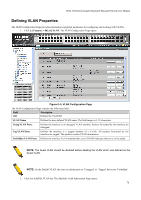
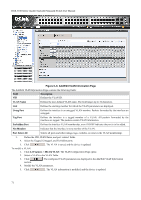
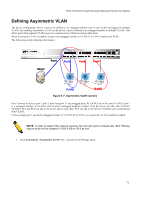
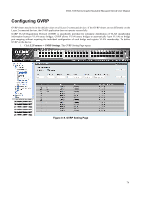
DGS-3100 Series Gigabit Stackable Managed Switch User Manual the ingress port. If it does not, the packet is dropped. If it has the same VID, the packet is forwarded and the destination port transmits it on its attached network segment. This process is referred to as ingress filtering, and is used to conserve bandwidth within the switch, by dropping packets that are not on the same VLAN as the ingress port at the point of reception. This eliminates the subsequent processing of packets that is just dropped by the destination port. Default VLANs The switch initially configures one VLAN, VID = 1, called 'default.' The factory default setting assigns all ports on the switch to the 'default.' Ports can be removed from the default VLAN by either setting the port on the default VLAN as a non-member, or if the port is configured as Untagged on another VLAN. Packets cannot cross VLANs. If a member of one VLAN wants to connect to another VLAN, the link must be through an external router. NOTE: If no VLANs are configured on the switch, then all packets are forwarded to any destination port. Packets with unknown source addresses are flooded to all ports. Broadcast and multicast packets are also flooded to all ports. An example is presented in this table: VLAN Name VID System (default) 1 Engineering 2 Marketing 3 Finance 4 Sales 5 Switch Ports 5, 6, 7, 8, 21, 22, 23, 24 9, 10, 11, 12 13, 14, 15, 16 17, 18, 19, 20 1, 2, 3, 4 Table 0-1. VLAN Example - Assigned Ports VLAN and Trunk Groups Trunk Groups (LAGs) can be added as member to a VLAN (similar to ports). The members of a trunk group have the same VLAN setting. Any VLAN setting on trunk group members applies to the other member ports. NOTE: In order to use VLAN segmentation in conjunction with port trunk groups, the port trunk group(s) can first be set, and then the VLAN settings may be configured. Changing the port trunk grouping with VLANs already in place doesn't require reconfiguration of the VLAN settings after changing the port trunk group settings. VLAN settings automatically change in conjunction with the change of the port trunk group settings. VLAN Status The VLAN List displays VLANs, VLAN membership and membershiop type. This window displays the ports on the switch that are currently Egress or Tag ports. To view the following table, open the L2 features->VLAN folder and click the VLAN Status Link. This section contains the following topics: • Defining VLAN Properties • Configuring GVRP 69