D-Link DSN-610 User Manual for DSN-6110 & DSN-6110 with DSN-610 - Page 99
MPIO and MC/S.
 |
View all D-Link DSN-610 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 99 highlights
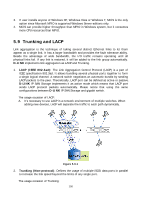
2. MC/S: MC/S (Multiple Connections per Session) is a feature of iSCSI protocol, which allows combining several connections inside a single session for performance and failover purposes. In this way, I/O can be sent on any TCP/IP connection to the target. If one connection fails, another connection can continue processing I/O without interruption to the application. Figure 5.8.2 Difference: MC/S is implemented on iSCSI level, while MPIO is implemented on the higher level. Hence, all MPIO infrastructures are shared among all SCSI transports, including Fiber Channel, SAS, etc. MPIO is the most common usage across all OS vendors. The primary difference between these two is which level the redundancy is maintained. MPIO creates multiple iSCSI sessions with the target storage. Load balance and failover occurs between the multiple sessions. MC/S creates multiple connections within a single iSCSI session to manage load balance and failover. Notice that iSCSI connections and sessions are different than TCP/IP connections and sessions. The above figures describe the difference between MPIO and MC/S. There are some considerations when user chooses MC/S or MPIO for multipathing. 1. If user uses hardware iSCSI off-load HBA, then MPIO is the only one choice. 2. If user needs to specify different load balance policies for different LUNs, then MPIO should be used. 99